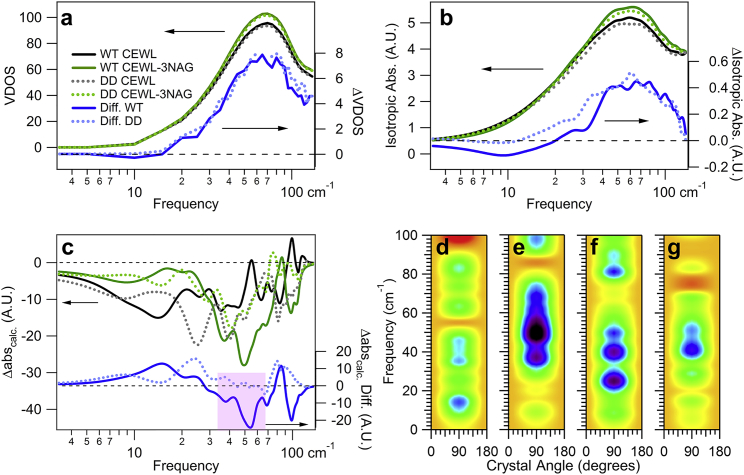
Figure 5.
Sensitivity of intramolecular vibrations to mutations. Calculated (a) VDOS and (b) isotropic absorbance for free and inhibitor bound WT and DD CEWL. The units for the difference (right axis) are the same as the left axis. These calculations reveal little difference in the dynamics for the two proteins, whereas (c) the relative anisotropic absorbance at 90°, shows the directionality of vibrations clearly changes. The spectra (a–c) are calculated for free WT CEWL (black solid line), 3NAG bound WT CEWL (green solid line), for free DD CEWL (gray dashed line), 3NAG bound DD CEWL (green dashed line), and the difference spectra with binding for WT CEWL (blue solid line) and DD CEWL (blue dashed line). Calculated Δabs spectra of (d) a free WT CEWL, (e) a bound WT CEWL-3NAG inhibitor, (f) a free CEWL mutant, and (g) a bound CEWL-3NAG inhibitor mutant. The color scale follows that in Fig. 1; however, the range here is [−30, +15]. The symmetry for the anisotropic calculations reflects the experimental configuration. To see this figure in color, go online.