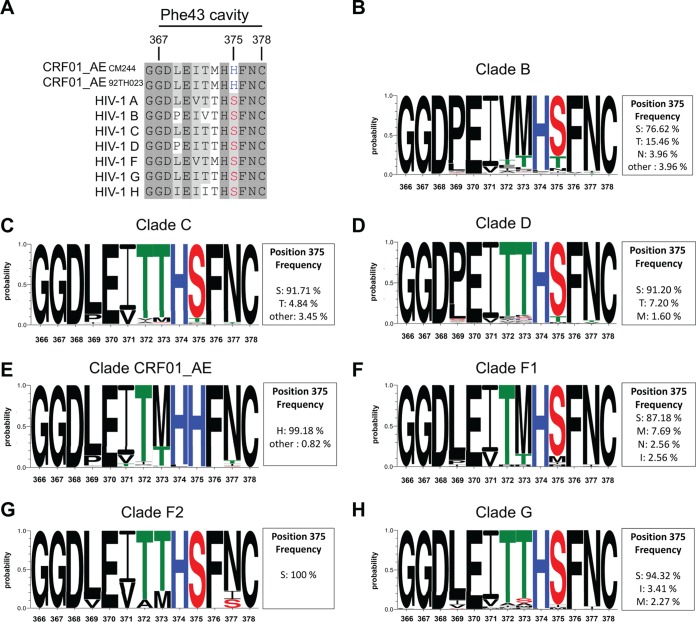
FIG 1.
Sequence alignment of gp120 residues flanking the Phe 43 cavity of different HIV-1 isolates. (A) Primary sequence alignment of gp120 residues flanking the Phe 43 cavity based on a single representative sequence from each clade, including HIV-1 clade A (GenBank accession number ABB29387.1), HIV-1 clade B (accession number K03455), HIV-1 clade C (accession number AAB36507.1), HIV-1 clade D (accession number P04581.1), HIV-1 clade F (accession number ACR27173.1), HIV-1 clade G (accession number ACO91925.1), and HIV-1 clade H (accession number AAF18394.1), and two CRF01_AE strains, CM244 (accession number AY713425) and 92TH023. Residue numbering is based on that of the HXBc2 strain of HIV-1. Identical residues are shaded in dark gray, and conserved residues are shaded in light gray. S375 is shown in red, and H375 is shown in blue. (B to H) Logo depictions of the frequency of each amino acid from the Phe 43 cavity at positions 366 to 378 in isolates from clade B, clade C, clade D, CRF01_AE, clade F1, clade F2, and clade G. The height of the letter indicates its frequency within the clade. The box beside each logo indicates the frequency of all the amino acids at position 375. The 2016 Los Alamos database-curated Env alignment was used as the basis for this figure, which contains 4,397 amino acid HIV-1 group M sequences (1,897 of subtype B, 1,363 of subtype C, 125 of subtype D, 39 of subtype F1, 9 of subtype F2, 88 of subtype G, and 486 of CRF01_AE).