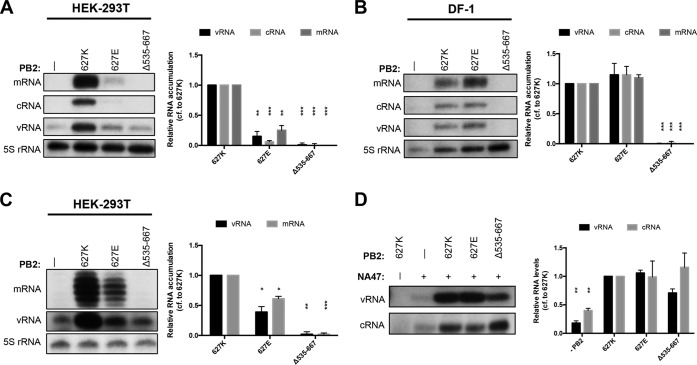
FIG 3.
The PB2 627 domain is required for polymerase activity in the cell. Human HEK-293T (A) or chicken DF-1 (B) cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing PA, PB1, wild-type or mutant PB2, NP, and segment 6 vRNA. Human HEK-293T cells (C) were cotransfected with plasmids expressing PA, PB1, wild-type or mutant PB2, and a 47-nt-long segment 6-derived vRNA. Accumulation of mRNA, cRNA, and vRNA was assessed by primer extension. The graphs show the mean intensity signal (with the mean intensity signal with no PB2 expressed subtracted) relative to that of wild-type PB2 627K polymerase from three independent biological replicates (n = 3), with error bars representing the standard errors of the means and the asterisks indicating a significant difference from the wild type (two-tailed one-sample t test) as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001. (D) Polymerase subunits PA-TAP, PB1 with an active-site mutation (PB1a), wild-type and mutant PB2, and segment 6-derived 47-nt-long vRNA or cRNA were coexpressed in HEK-293T cells and purified by IgG Sepharose chromatography. Levels of vRNA or cRNA that copurified with polymerase were assessed by primer extension. The graphs show the mean intensity signal (with the mean intensity signal with no RNA expressed subtracted) relative to that of wild-type 627K polymerase from three independent biological replicates (n = 3), with error bars representing the standard errors of the means and the asterisks indicating a significant difference from 627K (two-tailed one-sample t test) as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001.