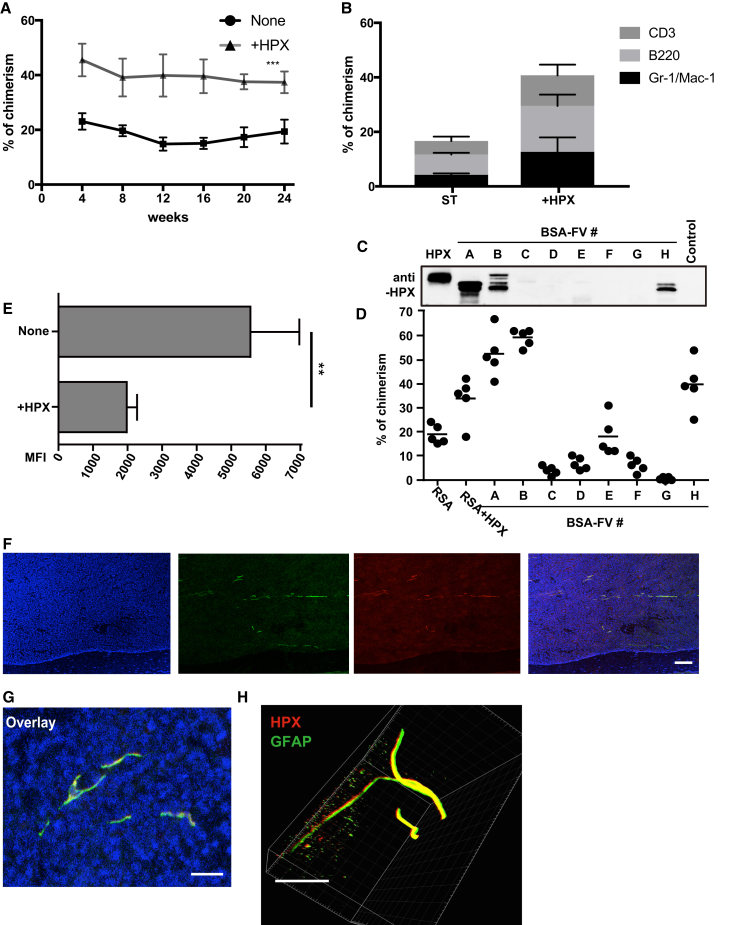
Figure 4.
The All-Recombinant Protein-Based Culture System Contributes to Identification of HSC Maintenance Factors Contained in BSA-FV
(A and B) The percentage PB chimerism from 40 CD34−KSL HSCs following culture for 1 week in the presence SCF, TPO, RSA, and with or without HPX (10 ng/mL) before transplantation into lethally irradiated recipient mice together with 106 BM competitor cells. PB chimerism measured over 24 weeks post transplantation (n = 4 or 5 mice per culture condition) and displayed as total PB chimerism (A) and blood-lineage chimerism (B) within the myeloid (Gr-1/Mac-1+), B cell (B220+), and T cell (CD3+) lineages at 12 weeks. Mean ± SD from two independent experiments.
(C) Immunoblotting for HPX of albumin-depleted BSA-FV.
(D) Lethally irradiated recipient mice were transplanted with 106 BM competitor cells and 40 CD34−KSL HSCs cultured for 1 week with 1% BSA-FV or 1% RSA with or without HPX (all in the presence of SCF and TPO). Percentage PB chimerism at 12 weeks post transplantation (n = 5 mice per BSA-FV culture condition). Mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
(E) Effect of HPX on ROS levels of in vitro cultured HSCs, as measured by flow cytometric analysis of HySOx staining. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values ± SD (n = 5 per culture condition).
(F and G) Fluorescence imaging of BM sections co-stained with anti-HPX (red), anti-GFAP (green), and DAPI (blue) antibodies. Scale bars: (F) 100 μm; (G) 4 μm.
(H) 3D fluorescence image of a representative tibia BM, stained with anti-HPX (red) and anti-GFAP (green). Scale bar, 150 μm.
Statistical significance denoted by ∗∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗∗p < 0.005 as determined by unpaired t test.