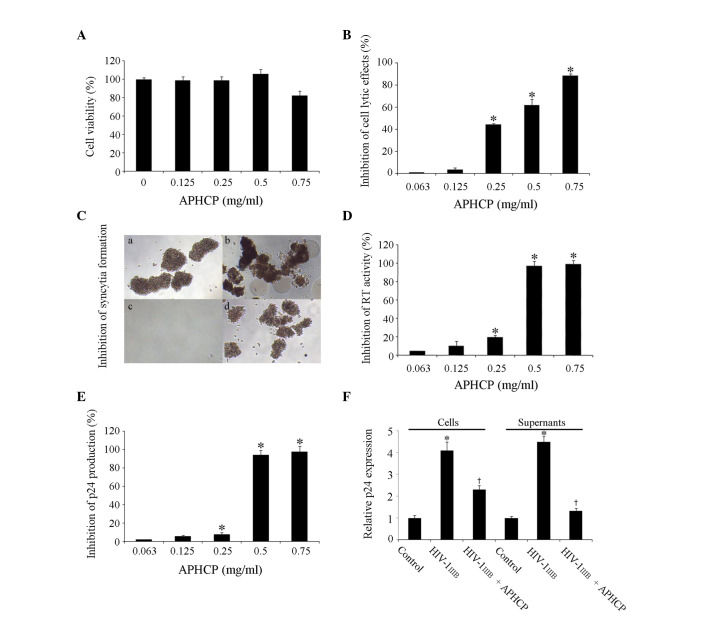
Figure 2.
Cytotoxity and anti-HIV-1 activity of APHCP. (A) Effect of APHCP on the viability of MT-4 cells, as measured by an MTT assay. APHCP did not affect the viability of MT-4 cells at concentrations less than 0.75 mg/ml. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). (B) Effect of APHCP on HIV-1IIIB-induced cell lysis, as measured by an MTT assay. Data are expressed as the percentage inhibition compared with HIV-1IIIB-infected untreated control cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05 compared with HIV-1IIIB-infected untreated cells. (C) Images of HIV-1IIIB-infected MT-4 cells. Syncytia formation was detected using an inverted light microscope (original magnification, ×100). Representative images from 3 independent experiments are presented. (a) Uninfected cell control, (b) HIV-1IIIB-infected cells, (c) HIV-1IIIB virus and APHCP, and (d) HIV-1IIIB infected cells with APHCP. (d) has less syncytia formation than in (b) or was similar to the uninfected in (a). (D) Effect of APHCP on RT activity. Data are expressed as the percentage inhibition compared with HIV-1IIIB-infected untreated control cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05 compared with HIV-1IIIB-infected untreated cells. (E) Effect of APHCP on p24 production by HIV-1IIIB-infected MT-4 cells. Data are expressed as the percentage inhibition compared with HIV-1IIIB-infected untreated control cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05 compared with HIV-1 IIIB-infected untreated cells. (F) Intracellular and secreted p24 protein expression levels were detected by western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05 compared with HIV-1IIIB-infected untreated control cells. †P<0.05 compared with HIV-1IIIB. APCHP treatment inhibited the lytic effects, syncytia formation, RT activity and p24 production of HIV-1 IIIB-infected MT-4 cells, in a dose-dependent manner. HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; APHCP, Alaska pollack skin hydroxyproline-containing collagen peptide; RT, reverse transcriptase.