Fig. 18.
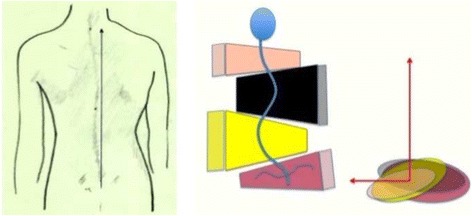
This figure shows the clinical picture and schema of blocks or regions for a four-curve pattern. This is called B type in Rigo classification. This type is characterized by a lumbosacral compensatory curve. The trunk is consequently divided into four blocks or regions, translated and rotated one against the other, collapsed on the concavities and expanded on the convexities. The three upper blocks, lumbar or thoracolumbar, main thoracic and proximal thoracic are imbalanced to the left according to the most caudal pelvic block (including this last the central sacral line). Pelvis is translated to the right according to the polygon of sustentation, so right hip joint is in relative adduction in comparison with left hip joint. This description corresponds to a “right 4C or B type.” The mirror case exists for a left convex thoracic curve combined with right lumbar or thoracolumbar and it is called “left 4C or B type”
