Figure 2. Establishing a cell-based assay system that inhibits WNT1 expression through stabilizing the G-quadruplex structure formed at its promoter.
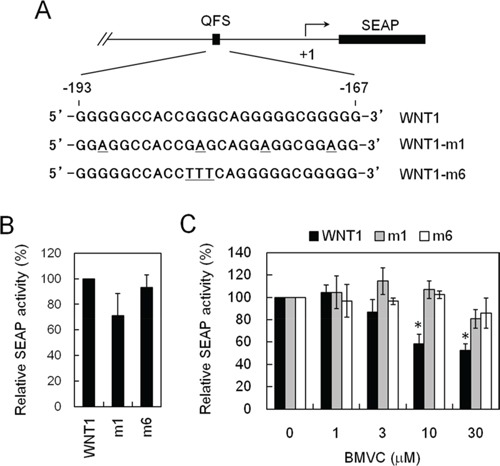
A. Schematic diagrams showed the mutation sites of WNT1 in reporter assays. The G-quadruplex-forming sequences of Wnt1 (wild-type), Wnt1-m1, or Wnt1-m6 (Wnt1 mutations) were indicated. B. Wnt1-m1 and m6 mutations did not affect the basal expression level of WNT1. The H1299 cells harboring wild-type, WNT1-m1, and Wnt1-m6 reporters were analyzed for their basal expression activity. The relative phosphatase activities of wild-type, WNT1-m1, and WNT1-m6 mutant were presented using the wild-type level as 100%. C. BMVC repressed WNT1 expression required G-quadruplex structure formation. The H1299 cells harboring wild-type, WNT1-m1, and WNT1-m6 reporters were incubated with the indicated concentrations of BMVC for 2 days. The phosphatase activities were then analyzed using the activity of DMSO-treated cells as 100%. Asterisks indicate p < 0.05.
