Figure 1. Silencing of DUSP22 alternative transcripts in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas with monoallelic 6p25.3 breakpoints.
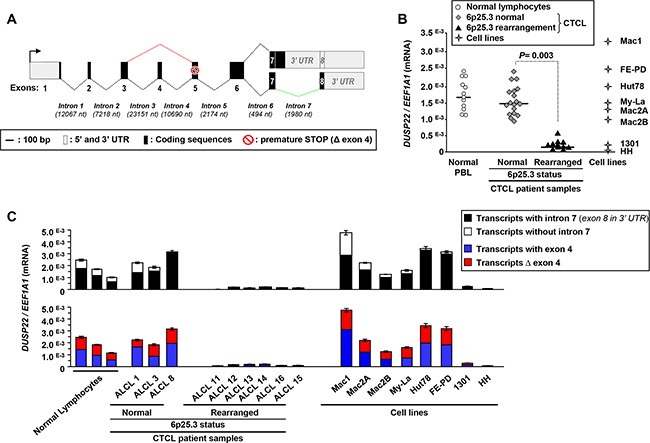
A. Schematic representation of DUSP22 alternative transcripts. Numbered boxes indicate the exons, with 5′ and 3′ untranslated (UTR) regions in grey and coding region in black. Nt: nucleotides. The black arrow indicates the position of the transcription initiation site. Dotted lines indicate the regular and alternative splicing events (in red, without exon 4; in green, without intron 7). The red symbol highlights the presence of a premature STOP codon which is in frame in Δ exon 4 transcripts. B. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of DUSP22 transcript levels (forward primer within exon 1 and reverse primer overlapping the junction between exons 6 and 7), normalized by EEF1A1 expression, in normal peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL), cutaneous T-cell lymphomas cases (CTCL) with or without 6p25.3 rearrangements, and lymphoid T-cell lines. Mean from independent measurements are shown. C. DUSP22 alternatively spliced transcipts levels were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR, normalized by EEF1A1 expression, in normal PBL, CTCL cases and lymphoid T-cell lines. Mean ± SEM from independent measurements are shown. For transcripts with and without intron 7 (Top panel), the common forward primer was within exon 1 and isoform-specific reverse primers were either at the beginning of intron 7, or at the beginning of exon 8. For transcripts with and without (Δ) exon 4 (Bottom panel), isoform-specific forward primers were overlapping either exons 3 and 4 or exons 3 and 5, respectively, and the common reverse primer was overlapping the junction between exons 6 and 7.
