Figure 1. Mechanisms of actions of HER-2 inhibitors.
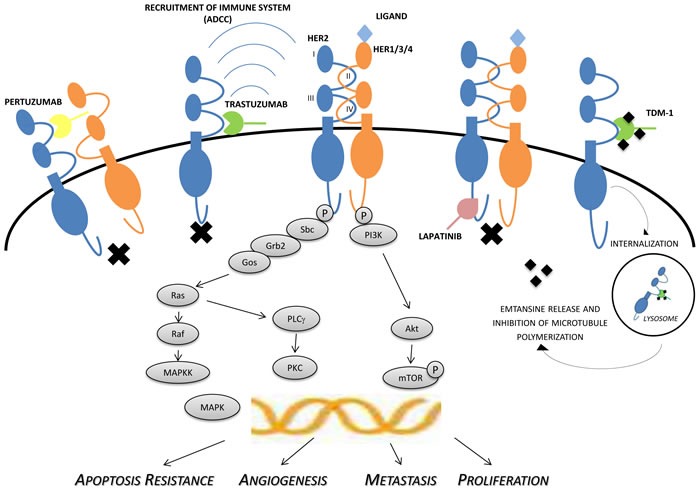
The figure shows the complex crosstalk between members of the HER-family and intracellular signaling, involved in proliferation, growth, invasion/metastases and angiogenesis. Activation of receptor kinase function occurs predominantly via ligand-mediated hetero- or homo-dimerization. In the case of HER-2, activation is also thought to occur in a ligand-independent manner, particularly when the receptor is found to be mutated or overexpressed. Trastuzumab is directed against the extracellular domain (IV) of HER-2, while pertuzumab binds to the extracellular dimerization domain (subdomain II). Immunologic mechanisms may also be involved in antitumor activity of trastuzumab, pertuzumab, and TDM-1, including ADCC. The potent small-molecule lapatinib inhibits the tyrosine kinases associated with HER-1 and HER-2, resulting in inhibition of phosphorylation and downstream signaling. ADCC: antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, HER: human epidermal growth factor receptor, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPKK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin, P: phosphate group, PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PKC: protein kinase C, PLCγ: phospholipase C-gamma, TDM-1: trastuzumab emtansine.
