Figure 4. TGR5/EGFR signaling contributes to the CDCA-induced ROS production and IL-1β secretion.
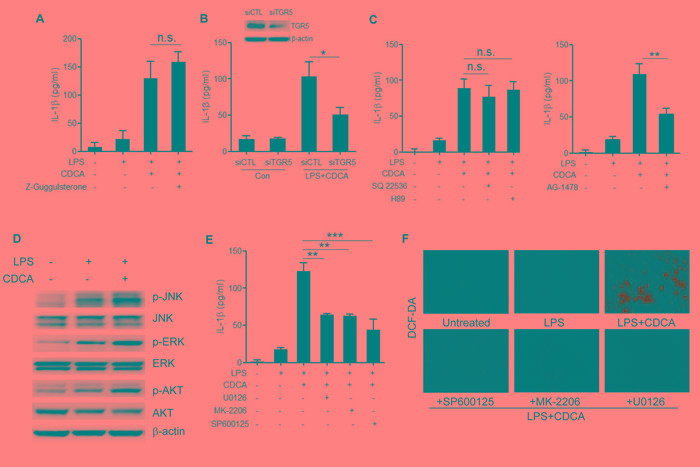
A. LPS-primed J774A.1 macrophages were treated with CDCA in the presence or absence of Z-Guggulsterone (20 μM). IL-1β in supernatants was analyzed by ELISA. B. Control siRNA (siCTL) or TGR5 siRNA (siTGR5) transfected J774A.1 macrophages were primed with LPS and then treated with CDCA for 24h. IL-1β in supernatants was analyzed by ELISA. Inset, Immunoblot analysis of TGR5 expression in siCTL or siTGR5 transfected cells. C. LPS-primed J774A.1 macrophages were treated with CDCA in the presence or absence of SQ22536 (400 μM), H89 (10 μM) or AG-1478 (30 μM). IL-1β in supernatants was analyzed by ELISA. D. Immunoblot analysis of phospho-JNK, total JNK, phospho-ERK, total ERK, phospho-AKT and total AKT of LPS-primed J774A.1 macrophages treated with or without CDCA. β-actin was immunoblotted as a loading control. (E-F) LPS-primed J774A.1 macrophages were treated with CDCA in the presence or absence of U0126 (10 μM), MK-2206 (10 μM) or sp600125 (25 μM). E. IL-1β in supernatants was analyzed by ELISA, F. Cells were incubated with DCF-DA probe for 1 h. Fluorescence images was used to exhibit the ROS formation. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; n.s.: no statistically significant difference (p > 0.05). Error bars indicate s.e.m. The data shown are representative of 3 individual experiments yielding similar results.
