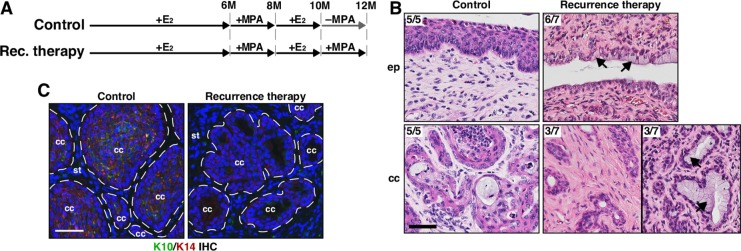
Figure 3. MPA fails to regress recurrent cervical cancer.
(A) Treatment regimens are shown. Mice were enrolled in the study at 4−6 weeks of age. (B) Recurrent cervical cancer remains after MPA therapy. Representative images of H&E−stained cervical tissue sections are shown. The number of mice with presented histology is indicated at the upper left corner. Black arrows point to cells with clear cytoplasm, indicative of mucinification. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) K10 expression is decreased in recurrent cervical cancer treated with MPA. Cervical cancer sections were stained for K10 (green) and K14 (red). K14 stains cancer cells and K10 is a marker for differentiated squamous cells. Nuclei are shown in blue. Dotted lines separate cervical cancer (cc) from stroma (st). Scale bar, 50 μm.