Figure 5. Multifunctional JCV-specific CD8+ T cells: The ability of epitope-specific CD8+ T cells to secrete the cytokines IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2 after stimulation with peptides was evaluated by intracellular flow cytometry staining.
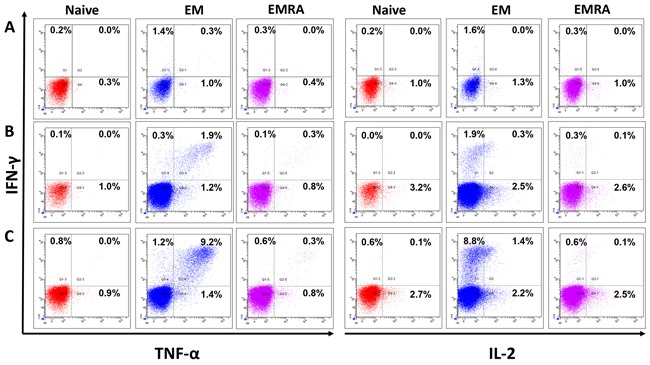
One representative flow cytometry data-set out of four independent experiments is displayed. The functional CD8+ T cells were divided into naïve (TN), effector memory (TEM) and effector memory RA+ (TE/EMRA) populations based on the expression of cell surface markers, CCR7 and CD45RA, respectively. First, cells were gated on lymphocytes and dead cells were excluded using the live/dead stain, NEAR. Cells were then gated on CD8+ T cells and subsequently either on the naïve (CCR7+, CD45RA+), the effector memory (EM) (CCR7- CD45RA-) or the effector memory RA (EMRA) (CCR7- CD45RA+). The cells were analyzed for intracellular expression of the inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2. CD8+ T cells were stimulated and restimulated with T2 cells loaded with: A. no peptide, B. JCV-p117 nonamer and C. JCV-p288 nonamer peptides, respectively. Flow cytometry dot-plots were analyzed for the co-expression of IFN-γ and TNF-α (left panel) and IFN-γ and IL-2 (right panel) in all three T cell subpopulations.
