Figure 2. Mapping of the Myc:CaM interaction domain.
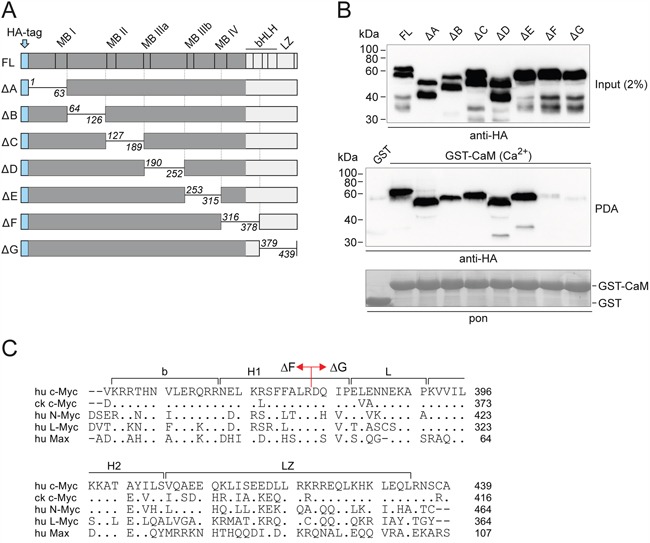
A. Schematic depiction of full-length (FL) human c-Myc and scanning deletion (Δ) mutants. The mutant proteins lack residues 1-63 (A), 64-126 (B), 127-189 (C), 190-252 (D), 253-315 (E), 316-378 (F), and 379-439 (G), respectively [20, 21]. bHLH, basic region/helix-loop-helix; LZ, leucine zipper; MB, Myc box; HA, hemagglutinin. B. Full-length c-Myc and the deletion mutants were expressed in QT6 cells. Whole cell lysates were used for pull-down experiments with GST-CaM in the presence of 0.5 mM CaCl2 (Ca2+), and with GST as negative control. An aliquot of the cell lysate (input, upper panel) and eluted proteins from the pull-down assay (PDA, middle panel) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using HA-specific antibodies. A section of the membrane with Ponceau S-stained GST bait proteins is shown (pon, lower panel). C. Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the bHLH-LZ domains of human (hu) c-Myc, chicken (ck) c-Myc, and human L-Myc, N-Myc, and Max. Identities with the human c-Myc sequence used as reference are indicated by dots, gaps are marked by dashes. On the human c-Myc sequence, the border between the ΔF and ΔG deletions (cf. panel A) is indicated.
