Figure 3. The role of immune cells during liver regeneration.
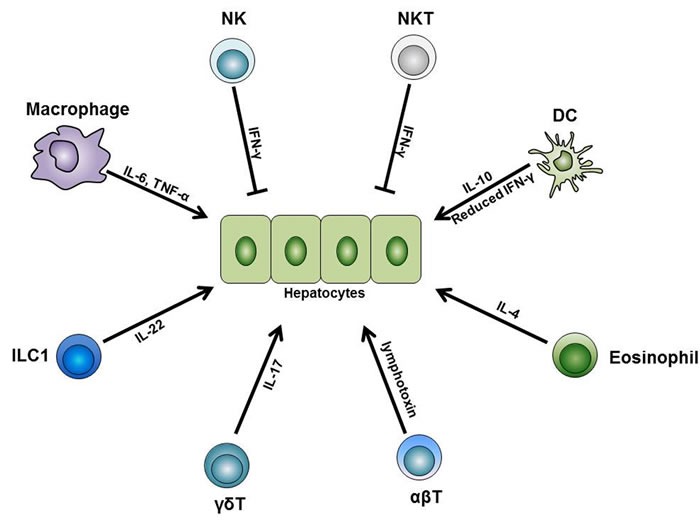
Different subsets of the innate and adaptive immune cells are indispensable for normal liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Among these cells, liver macrophages produce IL-6 and TNF-α and initiate the regeneration process after partial hepatectomy. Besides, liver DCs upregulate their IL-10 expression level while downregulate their IFN-γ level, thus facilitate liver regeneration. In addition, liver eosinophil-derived IL-4 also promotes the regeneration process. Furthermore, γδT cell-derived IL-17 and ILC1-derived IL-22 are both necessary for normal regeneration. On the other side, NK and NKT cells play inhibitory roles in liver regeneration, and this is mainly dependent on the IFN-γ they secrete. Besides these innate immune cells, conventional αβT cells can secrete lymphotoxin and stimulate liver regeneration. Abbreviations: TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; ILC, innate lymphoid cell.
