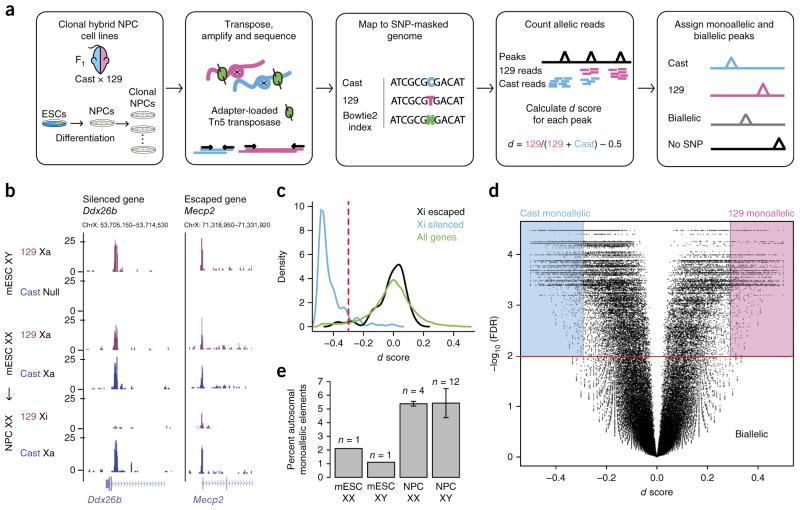
Figure 1.
Allele-specific ATAC–seq used to discover monoallelically accessible regulatory elements across the genome in mouse cells. (a) Experimental and analytic scheme. Cast and 129 mice were crossed, and F1 hybrid ESCs were isolated. ESCs were differentiated into NPCs and subcloned. ATAC–seq was performed on clonal cell lines. Sequencing reads were assigned to the 129 and Cast genomes. The d score of allelic imbalance was calculated for each ATAC–seq peak using SNP-informative reads. (b) Two examples of allele-specific ATAC–seq tracks on the X chromosome including the Ddx26b locus, which was silenced in differentiated cells, and the Mecp2 locus, which escaped silencing. Xa, active X chromosome; Xi, inactive X chromosome. (c) Distribution of d scores for ATAC–seq peaks at the promoters of silenced and escaped genes on the X chromosome as well as for all genes. The red dashed line corresponds to the cutoff of d score = −0.3 used to distinguish escaped from silenced elements. (d) Volcano plot showing d score versus –log10 (FDR) for all peaks in NPC clone XX1 across the genome. Background colors indicate how peaks are assigned on the basis of d score and FDR. (e) Percentage of total autosomal ATAC–seq peaks that are monoallelic in ESCs and NPCs derived from females and males. Error bars show s.d. across the number of clones indicated.