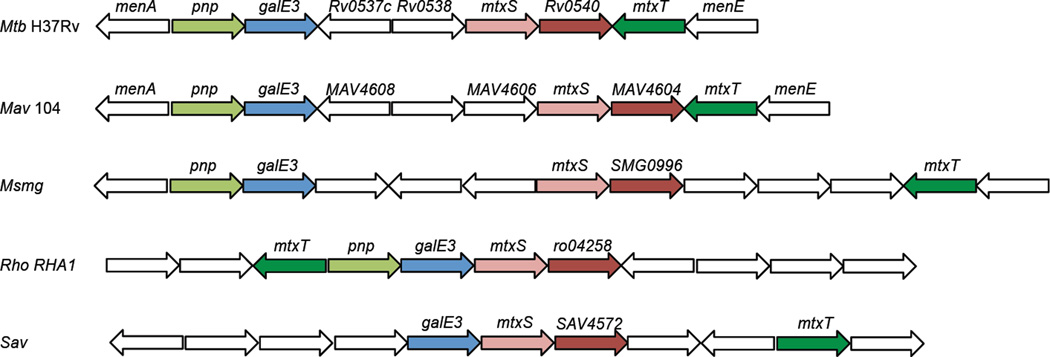
Figure 2. Representation of the MTX gene cluster in M. tuberculosis and other Actinomycetes.
Mtb H37Rv, Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv; Mav 104, Mycobacterium avium strain 104; Msmg, Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155; Rho RHA1, Rhodococcus sp. RHA1; Sav, Streptomyces avermitilis MA-4680. Similarly colored genes are orthologs. White genes are thought to be unrelated to the MTX biosynthetic pathway. Genes are not drawn to scale. Pnp, MTA phosphorylase; GalE3, putative NAD-dependent 5´-methylthioribose-nucleotide-3-epimerase; MtxS, decaprenyl-phosphoryl-MTX synthase; Rv0540 (and orthologs, MAV4604, SMG0996, ro04258, SAV4572), nucleotide-5´-methylthioribose synthase; MtxT, MTX-transferase. The pnp gene of S. avermitilis (SAV3679) is found in a different region of the genome. Rv0537c and MAV4608 display sequence similarities with the 5´-methylthioribose-1-phosphate isomerase from Bacillus licheniformis and are likely to be involved in the methionine salvage pathway. Rv0538 encodes a conserved membrane protein; orthologs of this gene are lacking in the MTX clusters of M. avium, M. smegmatis, S. avermitilis and Rhodococcus RHA1.