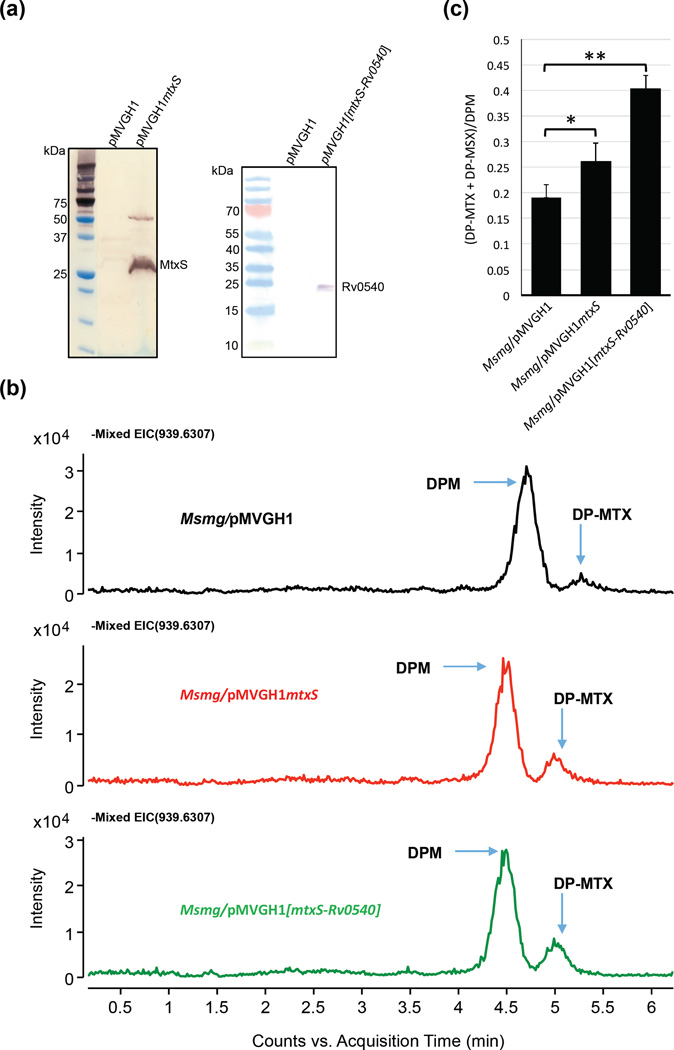
Figure 8. Effect of overexpressing mtxS and mtxS-Rv0540 on DP-MTX synthesis in M. smegmatis.
(a) Immunoblot analysis of MtxS and Rv0540 produced in M. smegmatis. M. smegmatis protein extracts prepared from mtxS and mtxS-Rv0540 overexpressing strains and a control strain carrying an empty pMVGH1 plasmid were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and the recombinant proteins (harboring an C-terminal His-tag) were detected using a monoclonal anti-polyhistidine monoclonal antibody (mouse Ig2a isotype; Sigma) as the first antibody and an anti-mouse IgG-alkaline phosphatase-conjugated antibody as the secondary antibody. Immune complexes were detected by monitoring alkaline phosphatase activity using NBT/BCIP (Thermo Scientific). The expected size of the recombinant Rv0540 protein is about 22.9 kDa; that of the recombinant MtxS protein is about 22.4 kDa; this protein consistently migrates with an apparent higher molecular weight, possibly due to its association with the membrane. A possible dimer of MtxS is also seen around 50 kDa.
(b) Negative ion LC/MS of DPM and DP-MTX from total lipids extracts of the M. smegmatis control strain (Msmg/pMVGH1) and the mtxS and mtxS-Rv0540 overexpressors. Decaprenyl-phosphoryl sugars were analyzed as described in Fig. 6.
(c) Relative amounts of DP-MTX and its sulfoxide form, DP-MSX, in the membranes of the M. smegmatis control strain, Msmg/pMVGH1, the mtxS overexpressor and the mtxS-Rv0540 overexpressor. The amounts of DP-MTX and DP-MSX relative to DPM were determined and the averages and standard deviations of two independent membrane preparations for each strain are shown. Statistical comparison (Student’s t-test) between control and overexpressing strains: ** p < 0.010; * p < 0.05.