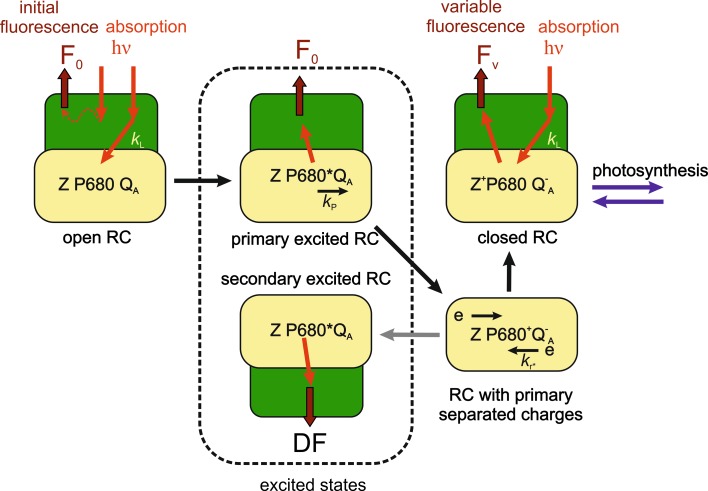
Fig. 6.
Illustration of the difference between F O and DF. Following absorption of a photon the excitation energy may be lost in the antenna and re-emitted as fluorescence (F O). The excitation energy may induce a charge separation, which may be followed by electron transfer to Q A or a recombination reaction. In the latter case the energy may again be lost as fluorescence (F O). Emission occurs at subnanosecond times following excitation. Fluorescence emission induced by recombination between Q −A and the PSII donor side leads to a delay in the emission time with the fluorescence emission occurring ~40 µs or longer following excitation and is called delayed fluorescence (DF) (Goltsev, unpublished data)