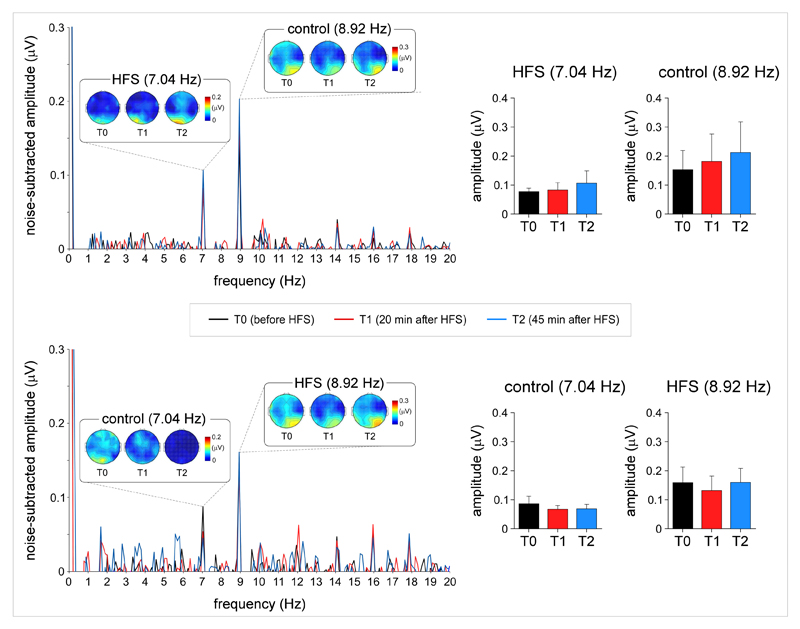
Figure 4.
Steady-state visual-evoked potentials. Steady-state visual-evoked potentials (SS-VEPs) elicited by concomitant periodic visual stimulation of the HFS arm and control arm at 7 Hz or 9 Hz. The frequency of the stimulation applied onto the HFS arm or the control arm was balanced across participants. Contrary to the N1 wave of visual-evoked potentials, HFS did not appear to exert any significant effect on the magnitude of the SS-VEPs, whose scalp topographies were maximal over occipital regions.