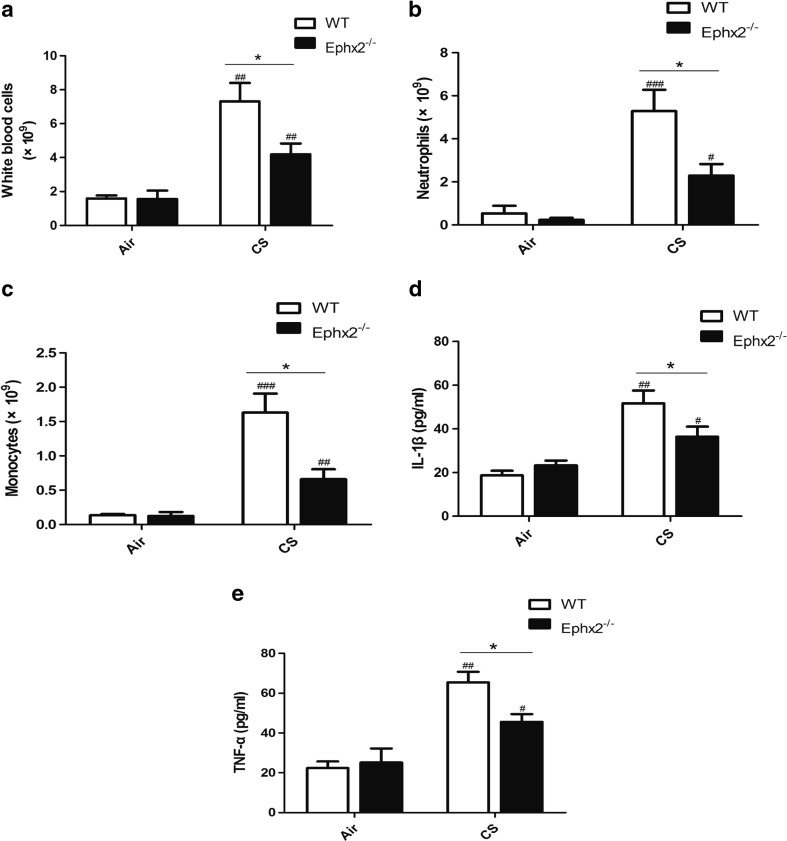
Fig. 4.
Ephx2−/− mice had reduced inflammation in response to CS. After 12 weeks of exposure to air or CS, BALF were obtained and inflammatory cells and TNF-α and IL-1β were quantified. a–c CS-exposed WT mice and CS-exposed Ephx2−/− mice had more leukocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes in BALF than air-exposed mice. CS-exposed Ephx2−/− mice had significantly fewer inflammatory cells in BALF. d, e TNF-α and IL-1β were increased in CS-exposed WT and CS-exposed Ephx2−/− mice than with air-exposed WT and air-exposed Ephx2−/− mice. CS-exposed Ephx2−/− mice had significantly lower TNF-α and IL-1β than CS-exposed WT mice. Results are expressed as means ± SD (n = 4 mice/group). # P < 0.05, significant difference from corresponding air-exposed mice; ## P < 0.01, significant difference from corresponding air-exposed mice; ### P < 0.001, significant difference from corresponding air-exposed mice; * P < 0.05, significant difference between CS-exposed WT mice and CS-exposed Ephx2−/− mice.