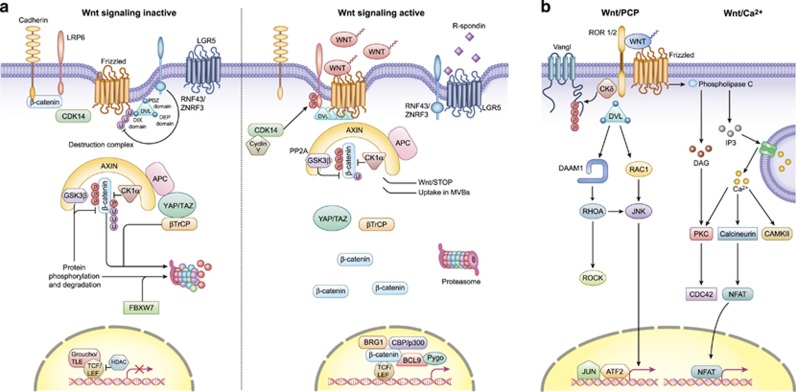
Figure 1.
Overview of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling. (a) In canonical Wnt signaling, absence of Wnt ligands (Wnt signaling inactive state, left) leads to phosphorylation of β-catenin by the destruction complex, which contains the scaffold protein Axin, APC and the kinases GSK3β and casein kinase (CK1α). In this state, β-catenin is phosphorylated by GSK3β, ubiquitinated by β-TrCP200 and targeted for proteasomal degradation. In the absence of nuclear β-catenin, a repressive complex containing TCF/LEF and transducing-like enhancer protein (TLE/Groucho) recruits HDACs to repress target genes. The canonical pathway is activated upon binding of secreted Wnt ligands (for example, Wnt3a and Wnt1) to Fzd receptors and LRP co-receptors (Wnt signaling active, right). LRP receptors are then phosphorylated by CK1α and GSK3β, which recruits Dishevelled (Dvl) proteins to the plasma membrane where they polymerize and are activated.201 The Dvl polymers inactivate the destruction complex, for example, by sequestration in multivesicular bodies. This results in stabilization and accumulation of β-catenin which then translocates into the nucleus. There, β-catenin forms an active complex with LEF (lymphoid enhancer factor) and TCF (T-cell factor) proteins by displacing TLE/Groucho complexes and recruitment of histone modifying co-activators such as CBP/p300, BRG1, BCL9 and Pygo (reviewed in Lien and Fuchs48). This transcriptional switch leads to a change of multiple cellular processes.49, 202 (b) Non-canonical Wnt signaling is defined by β-catenin-independent mechanisms of signal transduction. During Wnt/PCP signaling, Wnt ligands bind to the ROR-Frizzled receptor complex to recruit and activate Dvl.203 Dvl binds to the small GTPase Rho by de-inhibition of the cytoplasmic protein DAAM1 (Dvl associated activator of morphogenesis 1).204 The small GTPase Rac1 and Rho together trigger ROCK (Rho kinase) and JNK. This leads to rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and/or transcriptional responses via for example, ATF2 (activating transcription factor 2).205 Next to Dvl, Vangl, a key member of Wnt/PCP signaling is activated by phosphorylation in a Wnt5a-dependent manner.206 Wnt/Ca2+ signaling is initiated by G-protein triggered phospholipase C activity207 leading to intracellular calcium fluxes and downstream calcium dependent cytoskeletal and/or transcriptional responses.208