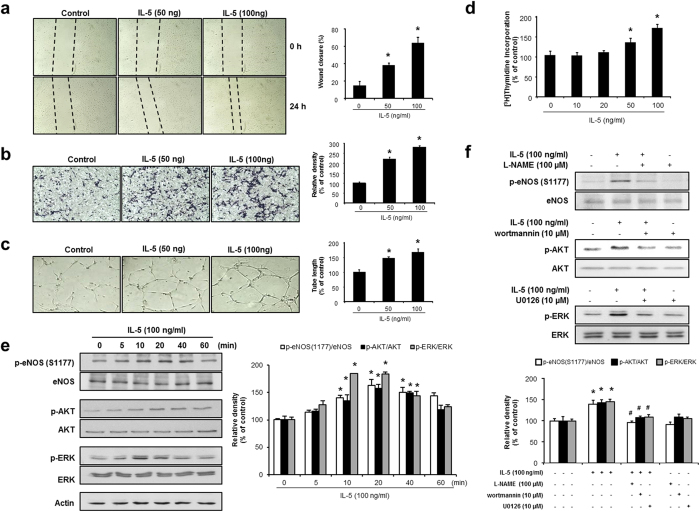
Figure 1. IL-5 induced the proliferation, migration, and colony tube formation and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and AKT/eNOS in HUVECs.
(a) Wound-healing assays revealed a significant induction in the wound closure rates of HUVECs after IL-5 stimulation for 24 h. (b) Invasion assay of HUVECs induced by IL-5 for 24 h. (c) Induction of capillary tube formation in IL-5-treated HUVECs. (d) Proliferative effect of IL-5 in HUVECs as evaluated by [3H]thymidine incorporation assay. (e,f) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2, AKT, and eNOS (S1177) in the presence or absence of U0126, wortmannin, and L-NAME, followed by IL-5 treated with HUVECs. All data are reported as the means ± SE from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with control, #P < 0.05 compared with IL-5 treatment.