Figure 3. Illustration of the three smart grid models.
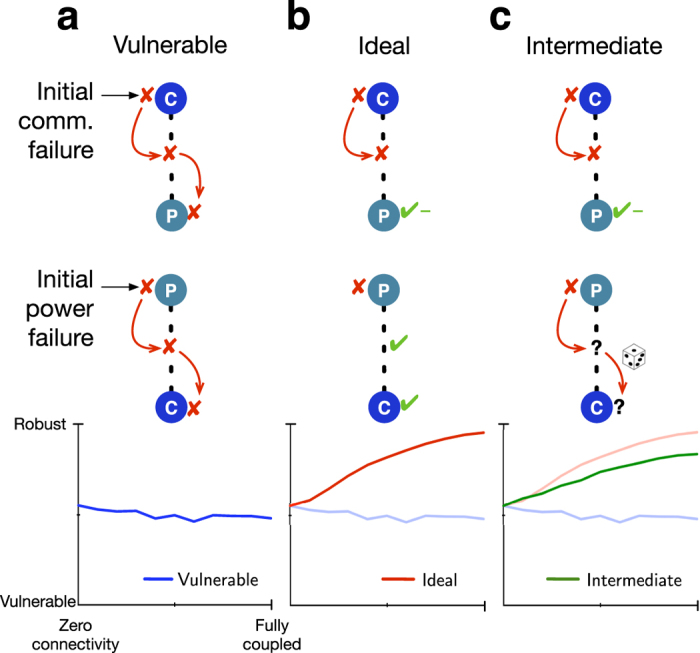
In the Vulnerable model (a), communication failures cause grid failures, and power failures cause communication failures, both with probability one. As the connectivity between the power grid and the communication network increases, the robustness of the network decreases. In the Ideal model (b), communication failures can degrade the ability to monitor and control power nodes, but power failures cannot return to cause additional communication failures. In this case, as connectivity increases, robustness increases. In the Intermediate model (c), communication failures degrade control performance as before, and power failures trigger communication failures probabilistically. Robustness is degraded, but still increases monotonically with connectivity.
