Figure 1.
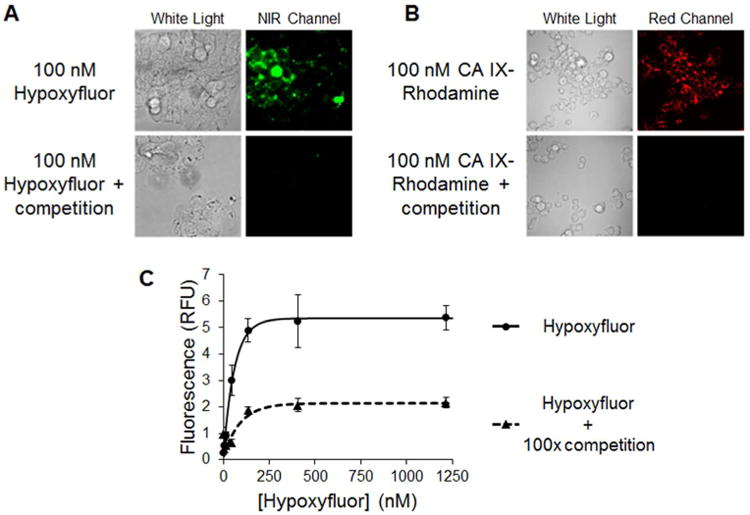
Binding of Hypoxyfluor and CA IX-targeted rhodamine to HT-29 cells. A) HT-29 cells were incubated with 100 nM Hypoxyfluor in the presence or absence of 100-fold excess of the CA IX inhibitor. After washing, the cell-associated fluorescence was imaged using a nonconfocal fluorescence microscope that could be excited at 747 nm; i.e. the wavelength where the NIR dye absorbs. Because the emitted light is not visible to the eye, the image is false colored green. B) HT-29 cells were similarly incubated with 100 nM CA IX-targeted rhodamine in the presence or absence of 100-fold excess CA IX inhibitor. After washing, the cell-associated fluorescence was imaged by confocal microscopy. C) HT-29 cells were incubated with various concentrations of Hypoxyfluor in the presence or absence of 100-fold excess CA IX inhibitor. After washing, the remaining fluorescence was quantitated by fluorescence spectroscopy. Error bars represent standard deviation.
