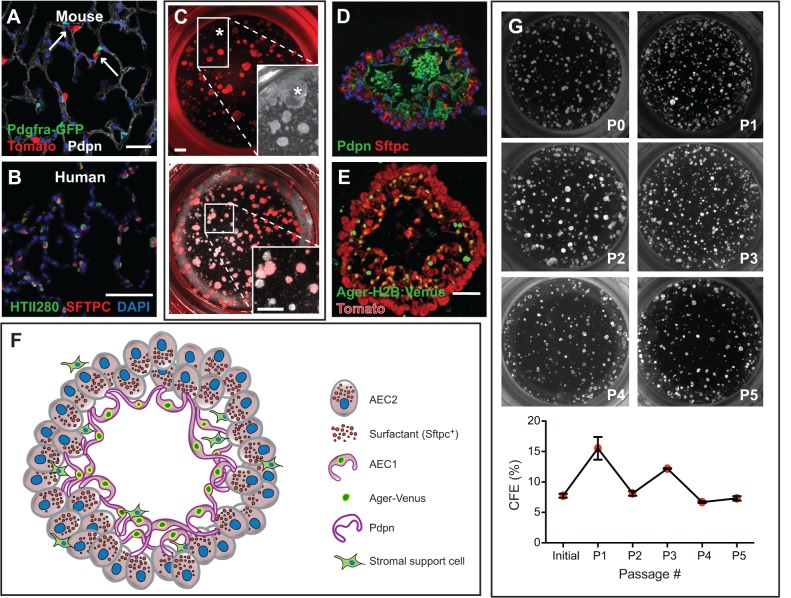
Fig. 4.
AEC2-derived alveolosphere culture. (A) Sftpc-CreERT2/+; R26R-tdTomato/+; Pdgfra-GFP/+ mice were injected with tamoxifen, leading to lineage labeling of ∼80% of AEC2s (Tomato+). Arrows point to Pdgfra-GFP+ lipofibroblasts in close proximity to lineage-labeled AEC2s. (B) HTII280 is a surface marker coexpressed with SFTPC to mark AEC2s in human lung. (C) Lineage-labeled AEC2s and GFP+ fibroblasts from the mouse lung in A were isolated by FACS and placed into the alveolosphere culture system in a ratio of 1:10, respectively. The asterisk in the top panel and in the brightfield inset marks a large, lobular, non-lineage-labeled sphere that is likely to have derived from a non-AEC2 epithelial cell. Without the lineage label it would have been incorrectly assumed that this sphere derived from an AEC2. The bottom panel and higher magnification inset shows an example of several non-lineage-labeled alveolospheres (lacking a fluorescent signal) that are likely to be derived from AECs that had not undergone recombination of the reporter allele. (D) Section of an alveolosphere showing Sftpc+ AEC2s on the outside and AEC1s (Pdpn+) on the inside. (E) Section of an alveolosphere showing lineage-labeled (Tomato+) Ager-H2B:Venus+ AEC1s on the inside. Green cells that are not lineage labeled are Pdgfra-GFP+ stromal cells. (F) Schematic illustrating the main cellular components of an alveolosphere. Currently, the precise way in which the AEC2s and AEC1s are connected to each other is not known. (G) Lineage-labeled AEC2s can be isolated and passaged (at day 14) at least five times without significant loss of CFE. Scale bars: 25 μm in A; 50 μm in B,E; 500 μm in C.