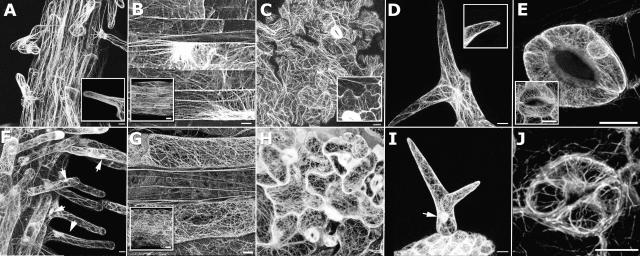
Figure 1.
Expression of GFP-fABD2 and GFP-mTalin in Arabidopsis. Confocal projections showing GFP-fABD2 (A–E) or GFP-mTalin (F–J) expression in roots (A and F), hypocotyls (B and G), leaf epidermis (C and H), trichomes (D and I), and stomata (E and J). A, Longitudinal cables in mature root epidermal cells and hairs; inset shows diffuse, irresolvable fluorescence in growing root hair tip. B, Longitudinal cables and transverse perinuclear arrays in hypocotyls that have ceased growth; inset shows similar arrangement of AFs in immature hypocotyls. C, Pavement epidermal cells show randomly arrayed transvacuolar bundles; inset shows expanding epidermal cells. D, Longitudinal bundles in young trichomes; inset shows diffuse tip fluorescence. E, Intricate cortical and simple perinuclear arrays in guard cells; inset shows transversely oriented AF bundles. F and I, Helical arrays of filaments in root hairs and trichomes; nucleoplasmic labeling is evident (arrows). G, H, and J, Randomized networks of short, curved filaments in hypocotyl, leaf epidermis, and stomata. G, Mature hypocotyl tissue; inset shows immature hypocotyl. All images are confocal projections composed of 85 (A and F), 63 (B and G), 54 (D and I), 35 (B inset and G inset), 15 (E, J, and E inset), or 10 (C, H, C inset, and D inset) optical sections. Scale bar = 10 μm (A–J) or 20 μm (B and G, inset).