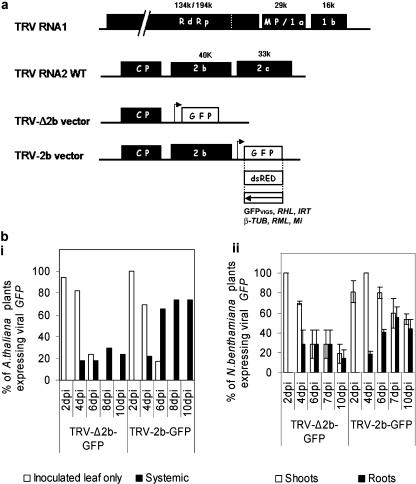
Figure 1.
Invasion of roots by TRV. a, Genomic organization of wild-type TRV RNA1 and TRV RNA2, and TRV-derived vectors used for expression of foreign protein and VIGS with modified RNA2 deleted from 2b and 2c protein or only 2c protein for, respectively, TRV-Δ2b and TRV-2b vectors. The TRV ORFs are represented in black boxes (not to scale) and correspond to the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), 1a or movement protein (MP), 1b or 16-K protein, coat protein (CP), 2b and 2c proteins. The size of the encoded proteins is indicated. Arrow represents the position of the duplicated subgenomic CP promoter driving the expression of inserted coding cDNA (GFP or DsRED represented in white boxes) or noncoding cDNA for silencing represented in white box and the name of corresponding target genes. b, Movement of TRV-Δ2b-GFP and TRV-2b-GFP vectors over 10 d. Subsection i, Virus movement in Arabidopsis shoots. (subsection i, TRV-Δ2b-GFP, n = 17; TRV-2b-GFP, n = 23). Virus movement in whole N. benthamiana plants (subsection ii, TRV-Δ2b-GFP, n = 26 ± se; TRV-2b-GFP, n = 45 ± se). GFP fluorescence was viewed using a stereofluorescence microscope (MZFLIII; Leica, Deerfield, IL). Filter set GFP3, excitation 450/90 nm; emission 500/50 nm).