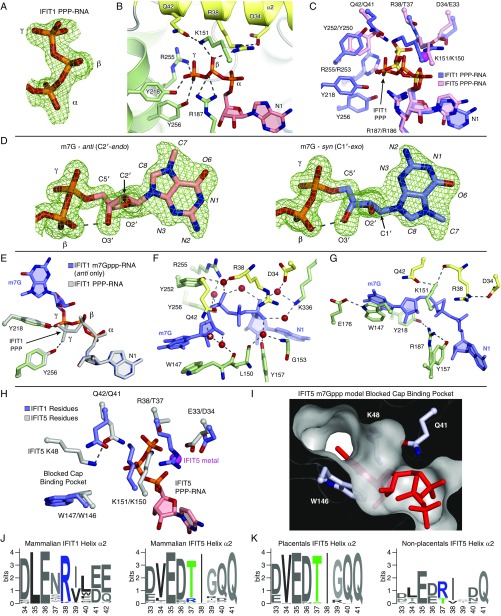
Fig. S3.
IFIT1 PPP- and m7Gppp- binding mechanism. (A) Simulated annealing 2Fo–Fc omit map of the PPP moiety contoured at 1σ. (B) Cartoon/stick representation of residues making specific contacts with the triphosphate group from PPP-RNA–bound IFIT1. (C) Superposition of PPP-RNA bound IFIT1 residues (blue carbons with orange phosphates) over PPP-RNA–bound IFIT5 residues (pink carbons with yellow-orange phosphates). The metal from PPP-RNA–bound IFIT5 is represented with a magenta sphere. The PPP from IFIT1 is in a different conformation, and makes additional H-bonds with Y256, Y218, and R187 not present in IFIT5. R38/D34 from IFIT1 are replaced with T37/E33 in IFIT5. Depending on the region, IFIT5 residue positions are offset by −1 or −2 compared with IFIT1 residue positions. (D) Simulated annealing 2Fo–Fc omit map of the m7Gppp moiety contoured at 1σ. Syn- and anti-configuration carbons are colored light blue and salmon, respectively. The hydrogen bond between the β-phosphate and the 3′-OH is indicated with the dashed line. Because of the constraints imposed on the base and bridging PPP binding, the ribose sugar pucker adapts by switching from a C2′-endo conformation in the anti-configuration, to C1′-exo in the syn-configuration. The final refined occupancies are ∼0.5 for each conformation. (E) Superposition of PPP-RNA bound IFIT1 (gray) over m7Gppp-RNA bound IFIT1 (green side-chain carbons and blue RNA carbons). The extended PPP conformation is common to both PPP- and m7Gppp-RNA binding, except that the γ-phosphate of m7Gppp- is repositioned at the entrance of the cap-binding pocket, away from Y256 and toward Y218, for more optimal m7G binding inside the pocket. (F) Water-mediated hydrogen bonds between IFIT1 and the m7Gppp moiety. Starting with the water at Q42 (*) and going clockwise, the isotropic B-factors of these waters are 27.6, 18.2, 17.6, 18.0, 19.4, 24.1, 15.3, 17.8 Å2, most of which are lower than the crystal isotropic B factor average (30.65 Å2). (G) Coordination between residues involved in m7Gppp-RNA binding. R187 is coordinated by Y218 and Y157; R38 by D34; K151 by R38 and Q42; and W147 by E176. (H) Superposition of m7Gppp-RNA–bound IFIT1 over IFIT5 PPP-RNA. In IFIT5, T37 facilitates recognition of a bent/compact PPP conformation that is further stabilized by a metal bound to the α- and γ-phosphates and coordinated by E33. This draws in K150 (which is H-bonded to T37), Q41 (which interacts with the PPP directly), and K48 (which is coordinated by Q41). (I) In IFIT5, K48 sits atop the cap-binding residue to block access to the cap-binding pocket as indicated by the attempt to model m7Gppp. In IFIT1, K49 from its cap-binding loop is facing the solvent. Also, in IFIT1, Q42 is not involved in binding the PPP directly. (J) WebLogo (weblogo.berkeley.edu/) sequence consensus of helix α2 from 86 IFIT1- and IFIT1B-like sequences, and 60 IFIT5-like sequences. (K) The mammalian IFIT5 sequences were split into placentals and nonplacentals (i.e., Tazmanian devil, opossum, platypus). Only nonplacental IFIT5-like sequences have an arginine at position 37 (human IFIT5 numbering).