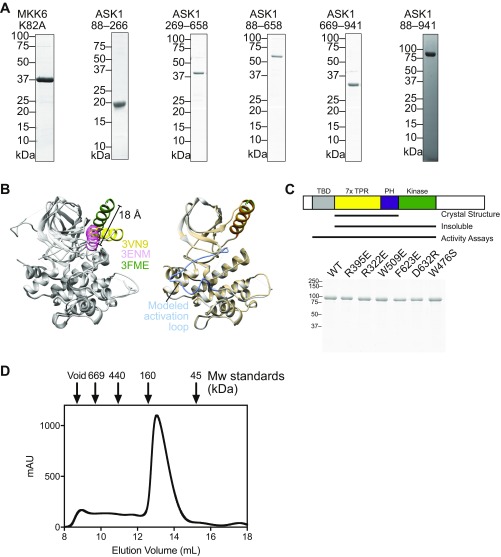
Fig. S1.
(A) Example purified sample proteins from each of the constructs used in this work. (B) Illustration of MKK6 conformational flexibility. (Left) An overlay of the three crystal structures of MKK6 currently available in the protein databank. All proteins are colored gray, with respective αC helices in yellow (2VN9), pink (3ENM), and green (3FME). The distance between the N terminus of the αC helix in 3ENM and 3FME is indicated. An illustrative model was created using Modeler to model in the disordered activation loop of structure 3FME. (Right) A comparison of 3FME with the Modeler output, with the activation loop indicated. The Modeler model is shown in Fig. 1F. (C) Purified point mutants of ASK1(88–941) used for the assays shown in Figs. 3C and 4B. A schematic summarizing the constructs is shown above, indicating that the construct containing only the central regulatory region and kinase was insoluble and so could not be tested in activity assays. (D) Preparative size-exclusion chromatography of ASK1(88–941) with molecular weight standards indicated. The majority of ASK1 protein elutes later than the 160-kDa marker, consistent with it behaving as a (∼100-kDa) monomeric species. Peak fractions elute at a concentration of ∼40 μM based on A280.