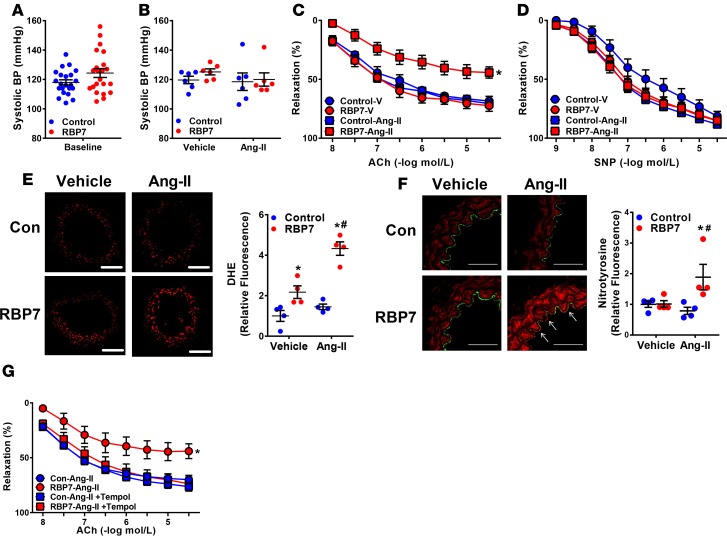
Figure 5. Role of RBP7 in response to Ang-II.
(A) Systolic BP was measured in control and RBP7-deficient mice at baseline by tail cuff. This is an independent replication cohort from that shown in Figure 1 to ensure that experiments performed at different times had similar range of BPs (n = 22, not significant by Student’s t test). (B) A subset of the mice used in panels C and D were first treated with a subpressor dose of Ang-II (120 ng/kg/min, 2 weeks) or vehicle (isotonic saline) and BP was measured by tail cuff to confirm the absence of a pressor response (n = 6, not significant by ANOVA). The robust hypertensive response to a pressor dose of Ang-II is shown in Supplemental Figure 4. (C and D) Vasodilation of the carotid artery from control and RBP7-deficient mice treated with vehicle or subpressor Ang-II was measured in response to acetylcholine (ACh) (C) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) (D) *P < 0.05 vs. RBP7–Ang-II by 2-way repeated measures (RM) ANOVA; n = 5–8 per group. (E and F) Representative dihydroethidium (DHE, E) fluorescence and nitrotyrosine immunofluorescence (F) staining conducted in carotid arteries from vehicle or Ang-II–infused control or RBP7-deficient mice. White arrows indicate nitrotyrosine-positive endothelial cells that costain with CD31. Scale bars: 100 μm (E) and 50 μm (F). Quantification of independent replicates is shown. *P < 0.05 RBP7 vs. control; #P < 0.05 RBP7–Ang-II vs. RBP7-vehicle by 2-way ANOVA; n = 4 per group. (G) Vasodilation of the carotid artery from control and RBP7-deficient mice infused with subpressor Ang-II for 2 weeks in the presence or absence of Tempol (1 mmol/l, 30 minutes) was measured in response to ACh. *P < 0.05 vs. all other curves by 2-way RM ANOVA; n = 5 per group. All data are the mean ± SEM. Ang-II, angiotensin II; RBP7, retinol-binding protein 7; V, vehicle; Con, control.