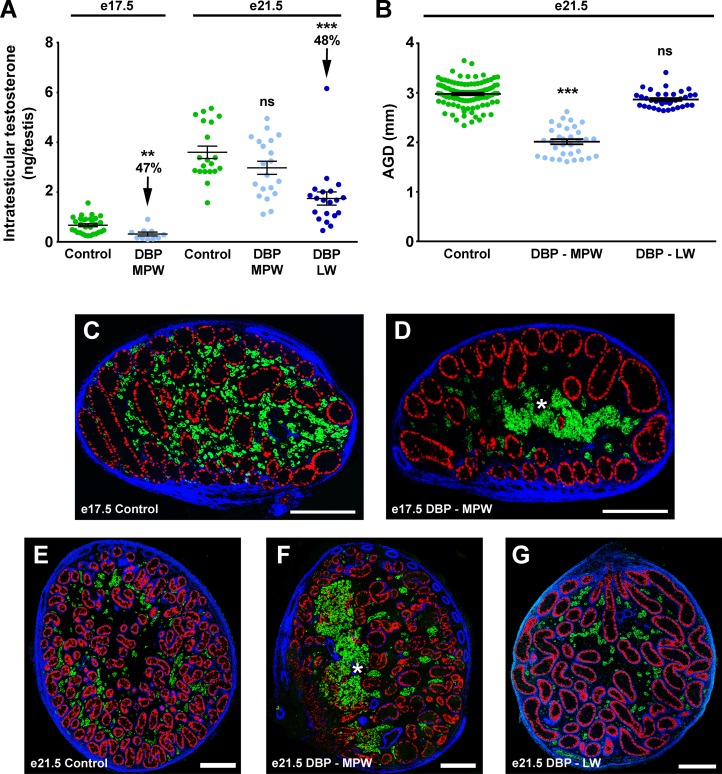
Figure 1. Effect of fetal exposure of rats to dibutyl phthalate during the masculinization programming window or immediately afterward (late window) on intratesticular testosterone, anogenital distance, and gross testis morphology at E17.5 and E21.5. Intratesticular testosterone (A), anogenital distance (B), and gross testis morphology (C–G) at E17.5 and E21.5. Note that E17.5 is during the MPW, E21.5 is at the end of the LW.
(A and B) Values are mean ± SEM, with analysis by 2-tailed Student’s t test or ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with respective control). (C–G) Sections were triple immunostained for SOX9 (red; Sertoli cells), 3β-HSD (green; Leydig cells), and smooth muscle actin (blue). Asterisks indicate abnormal aggregation of fetal Leydig cells (green). Scale bars: 200 μM. DBP, dibutyl phthalate; MPW, masculinization programming window; LW, late window; AGD, anogenital distance.