Table 2. Scope of enones a .
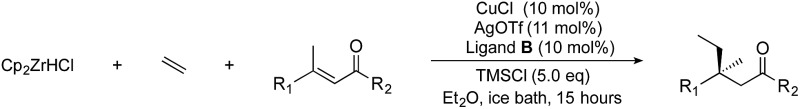
| ||||||
| Entry | Substrate |
Product |
Yield b [%] | ee c [%] | ||
| 1 |
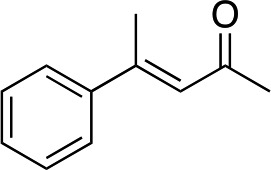
|
2b |
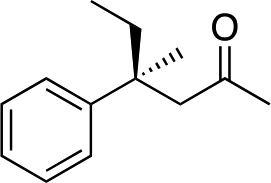
|
3b | 50 | 90 |
| 2 |
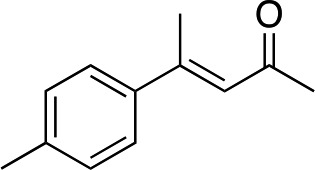
|
2c |
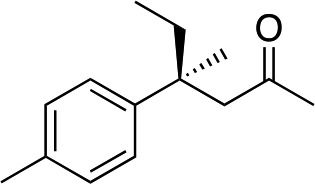
|
3c | 34 | 89 |
| 3 |
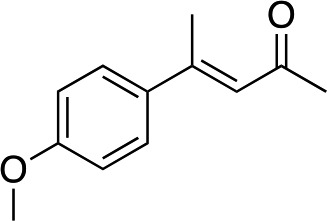
|
2d |

|
3d | 39 | 73 |
| 4 |
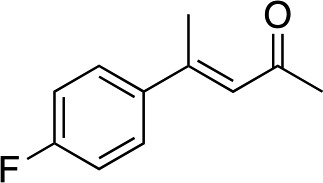
|
2e |
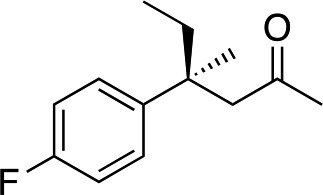
|
3e | 46 | 91 |
| 5 |
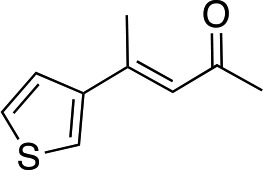
|
2f |
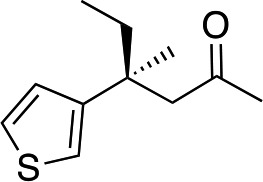
|
3f | 41 | 85 |
| 6 d |
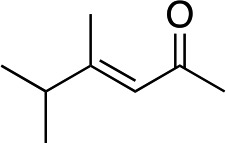
|
2g |
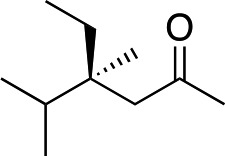
|
3g | 48 | 92 |
| 7 |
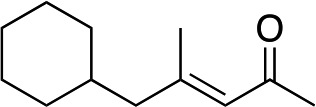
|
2h |
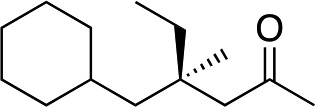
|
3h | 71 | 98 |
| 8 |
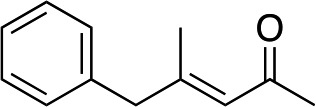
|
2i |
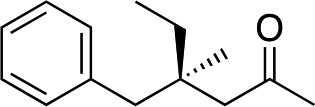
|
3i | 61 | 93 |
| 9 |
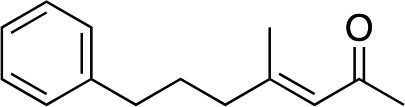
|
2j |
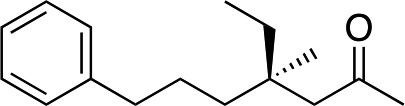
|
3j | 80 | 93 |
| 10 e |
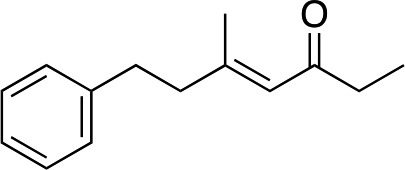
|
2k |
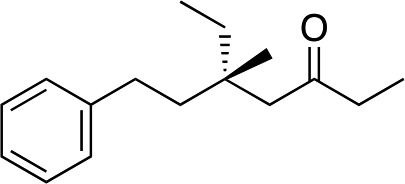
|
3k | 80 | 96 |
| 11 e |
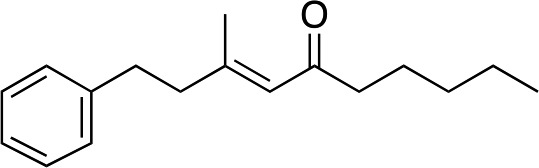
|
2l |
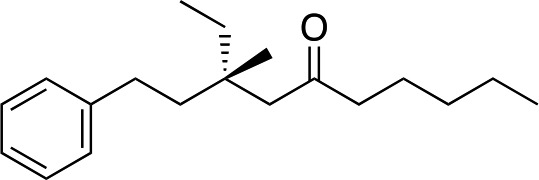
|
3l | 54 | 96 |
| 12 |
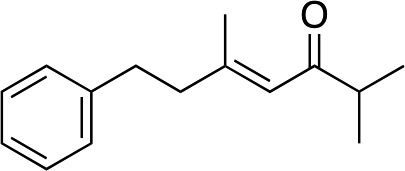
|
2m | — | — | — | — |
| 13 |
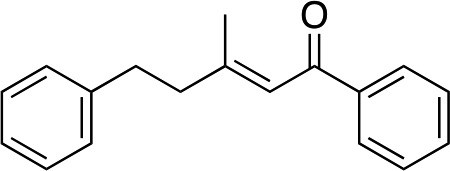
|
2n | — | — | — | — |
| 14 |
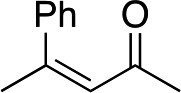
|
cis-2b |
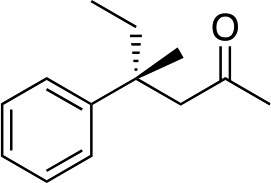
|
R-3b | 32 | 71 |
aReaction conditions: Ethylene balloon, [Cp2ZrHC1] (2 eq.), CH2C12; then enone (1 eq.), copper (10 mol%), ligand (10 mol%), silver (11 mol%), TMSC1 (5 eq.).
bYield of isolated product.
cee was determined by HPLC.
dee was determined by GC.
eThe enantiomer of ligand of B was used in these examples because the order of elution of the enantiomers aided ee determination.
