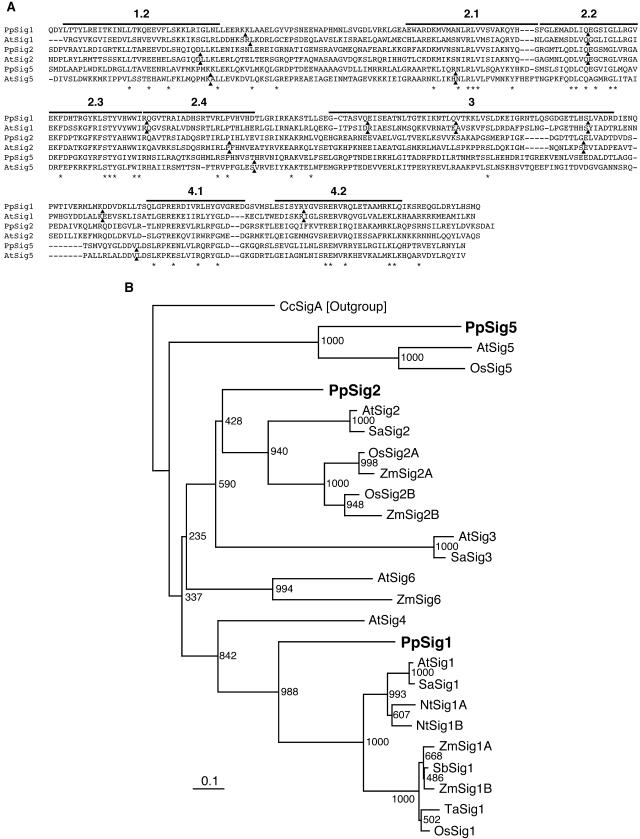
Figure 1.
A, Amino acid sequence alignment of the sigma factors from P. patens and Arabidopsis and comparison of intron sites. Sequences of conserved C-terminal regions through subdomains 1.2 to 4.2 of PpSIG1, PpSIG2, and PpSIG5 from P. patens and AtSIG1, AtSIG2, and AtSIG5 from Arabidopsis are aligned using the ClustalW program. Subdomains are indicated above the sequences. Intron positions are shown by black triangles. Identical amino acids are indicated by asterisks. B, A phylogenetic tree constructed using sigma factor sequences from various species. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method using approximately 260 aligned residues corresponding to the conserved regions 1.2 and 2.1 to 4.2. Numbers at each node represent bootstrap values out of 1,000 bootstrap resamplings. Bar indicates the distance corresponding to 10 changes/100 amino acid positions. PpSIG1 (AB059354), PpSIG2 (B059356), and PpSIG5 (AB189171) from P. patens are indicated by bold letters. Other sigma factors are as follows: AtSig1 (AB019942), AtSig2 (AB019943), AtSig3 (AB019944), AtSig4 (AB021119), AtSig5 (AB021120), AtSig6 (AB029916) from Arabidopsis, SaSig1 (Y15899), SaSig2 (AJ276656), and SaSig3 (AJ276657) from Sinapis alba, NtSig1A (AB023571) and NtSig1B (AB023572) from Nicotiana tabacum, OsSig1 (AB005290), OsSig2A (AB095094), OsSig2B (AB095094), and OsSig5 (AB096071) from Oryza sativa, SbSig1 (Y14276) from Sorghum bicolor, TaSig1 (AJ132658) from Triticum aestivum, ZmSig1A (AF058708), ZmSig1B (AF058709), ZmSig2A (AF099110), ZmSig2B (AF099111), and ZmSig6 (AF099112) from Zea mays, and CcSigA (D83179) from Cyanidium caldarium. CcSigA was used as the out group.