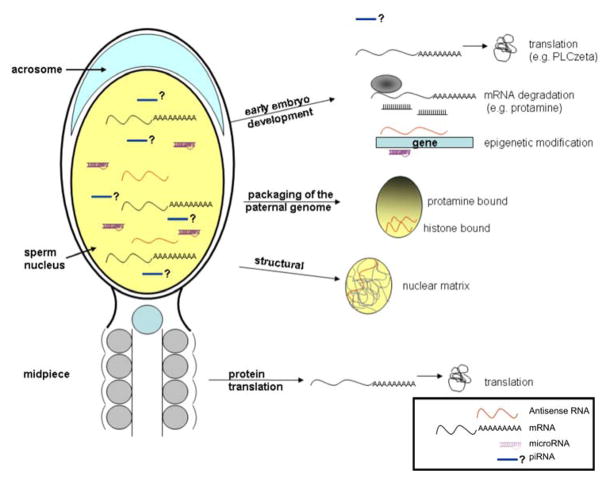
Figure 1.
Functions of sperm RNA. Different outcomes proposed for RNA populations, mRNA, antisense and microRNA, retained in mature spermatozoa. The RNA transferred to the oocyte at fertilization may function in early embryo development. mRNA could be translated, e.g. PLCzeta to sustain Ca2+ oscillation. Some mRNAs will be degraded, e.g. protamine. Antisense and microRNAs may epigenetically modify and modulate early embryonic gene expression. Sperm RNA may also have a structural role. For example, nuclear RNA may target chromosome regions remaining histone-bound. RNA located in the midpiece may be translated under certain conditions, e.g. capacitation.