Figure 2.
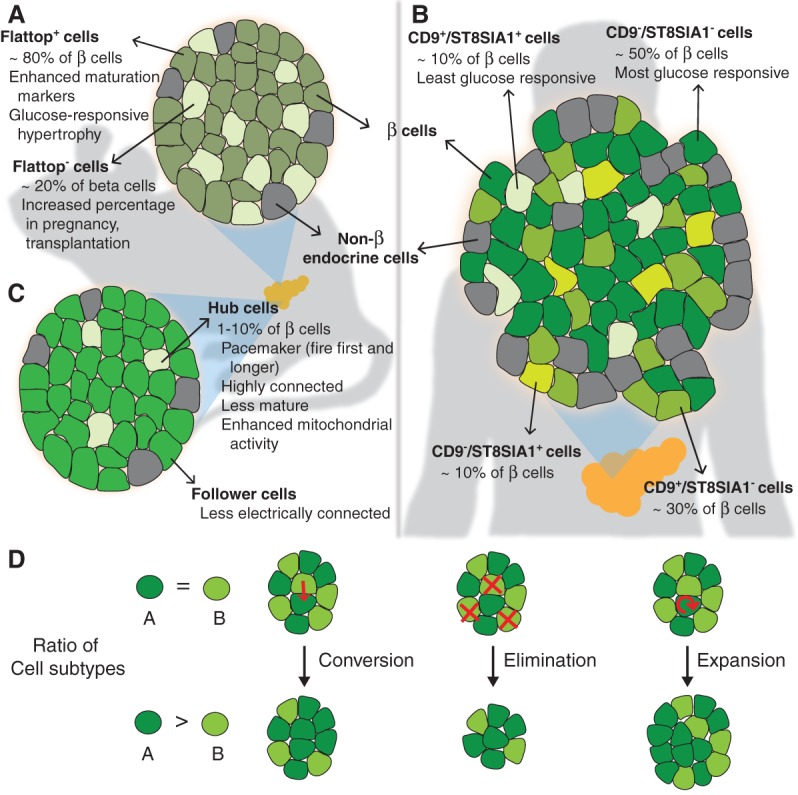
Markers of β-cell heterogeneity in adult islets. Three recent studies identified novel markers of β-cell heterogeneity and new β-cell subtypes (shades of green) in adult islets. (A) Flattop, a Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway effector, marks the major subpopulation of mouse β cells with a mature transcriptional profile. The ratio of Flattop-positive (Flattop+) to Flattop-negative (Flattop−) cells can change in response to different physiological contexts. (B) Differential expression of CD9 and ST8SIA1 demarcate four molecularly and functionally distinct subsets of human β cells. (C) Hub cells are highly connected pacemaker cells that instigate electrical signaling in follower cells in mouse islets. Hub cells express lower levels of some β-cell proteins and have enhanced metabolic response to glucose. (D) Processes such as conversion, selective elimination, and selective expansion can change the relative ratios of β-cell subtypes. Whether these processes occur for the different subtypes described during islet development, maturation, or disease progression remains to be determined.
