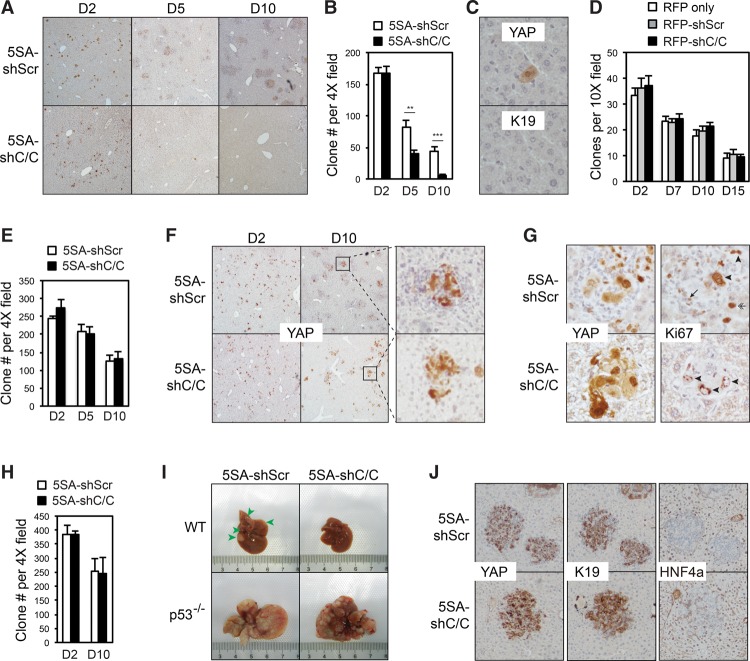
Figure 5.
YAP-induced TICAMs protect TICs from immune clearance. (A) Ccl2/Csf1 knockdown leads to the clearance of YAP-positive cells. Liver sections at post-injection day 2 to day 10 were stained for human YAP. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Quantification of YAP-positive clones in the same liver sections as those in A. Six views on sections from two mice for each genotype per time point were quantified. The experiments were reproduced three times. P-values were calculated by Student's t-test. (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001. (C) IHC staining of the remaining clones in serial liver sections of YAP-5SA-shCcl2/Csf1-injected mice at post-injection day 10. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (D) The expression of Ccl2 and Csf1 shRNAs does not cause cell clearance due to toxicity. Transposon elements carrying RFP alone or together with scrambled or Ccl2/Csf1 shRNAs were injected. The liver sections from post-injection day 2 to day 15 were quantified for RFP-positive clones. n = 2 mice in a single experiment. P-values > 0.05, as calculated by Student's t-test. (E) Experiments similar to those in B except that Rag1−/− mice were used. P-values > 0.05, as calculated by Student's t-test. The experiments were duplicated in the laboratory. (F) Rag1 knockout rescues TICAM-negative YAP-expressing clones. The liver sections of injected Rag1−/− mice from post-injection day 2 to day 10 were stained for human YAP. Results are representative of two independent experiments. (G) TICAMs are not required for the proliferation of YAP-expressing cells. Liver sections of injected Rag1−/− mice at post-injection day 10 were stained for human YAP and Ki67. Ki67+ YAP-expressing cells are denoted by arrowheads, a Ki67+ macrophage is denoted by an arrow, and a Ki67+ YAP− hepatocyte is denoted by a double arrow. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (H) The experiments were similar to those in B, except that p53 knockout mice were used. P-values > 0.05, as calculated by Student's t-test. The experiments were reproduced three times. (I) Knockout of p53 rescues YAP-induced tumorigenesis after the elimination of TICAMs. Representative liver photographs at 2 mo after injection. n = 3 mice. (J) Ccl2/Csf1 knockdown does not block YAP-induced hepatocyte dedifferentiation. The liver sections of injected p53−/− mice at post-injection day 10 were IHC-stained for the differentiation markers HNF4α and K19. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Values represent mean + SD.