Figure 3.
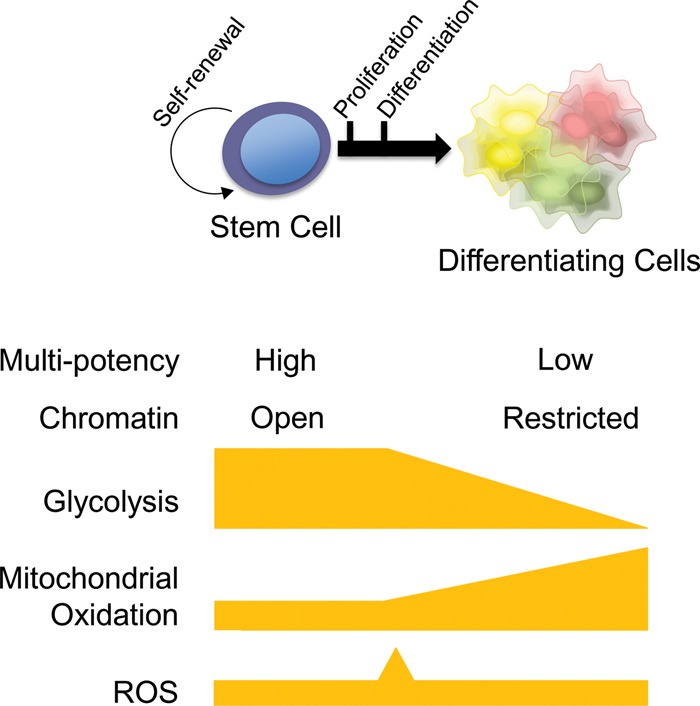
Unified summary of common metabolic features often observed during both PSC and adult stem cell differentiation. During self-renewal, both PSCs and adult stem cells maintain their multipotent capacity and a relatively open chromatin state. In conjunction with their epigenomic status, glycolysis and mitochondrial (glutamine or fatty acid) oxidation tend to be used, but total OxPhos flux and ROS levels typically stay low in a hypoxic environment. Proliferation of committed progenitors typically coincides with high glycolysis and a burst of ROS in a normoxic environment (see Fig. 2), while mitochondrial oxidation begins to rise. Further differentiation often leads to a decline in glycolysis and a further increase in mitochondrial oxidation.
