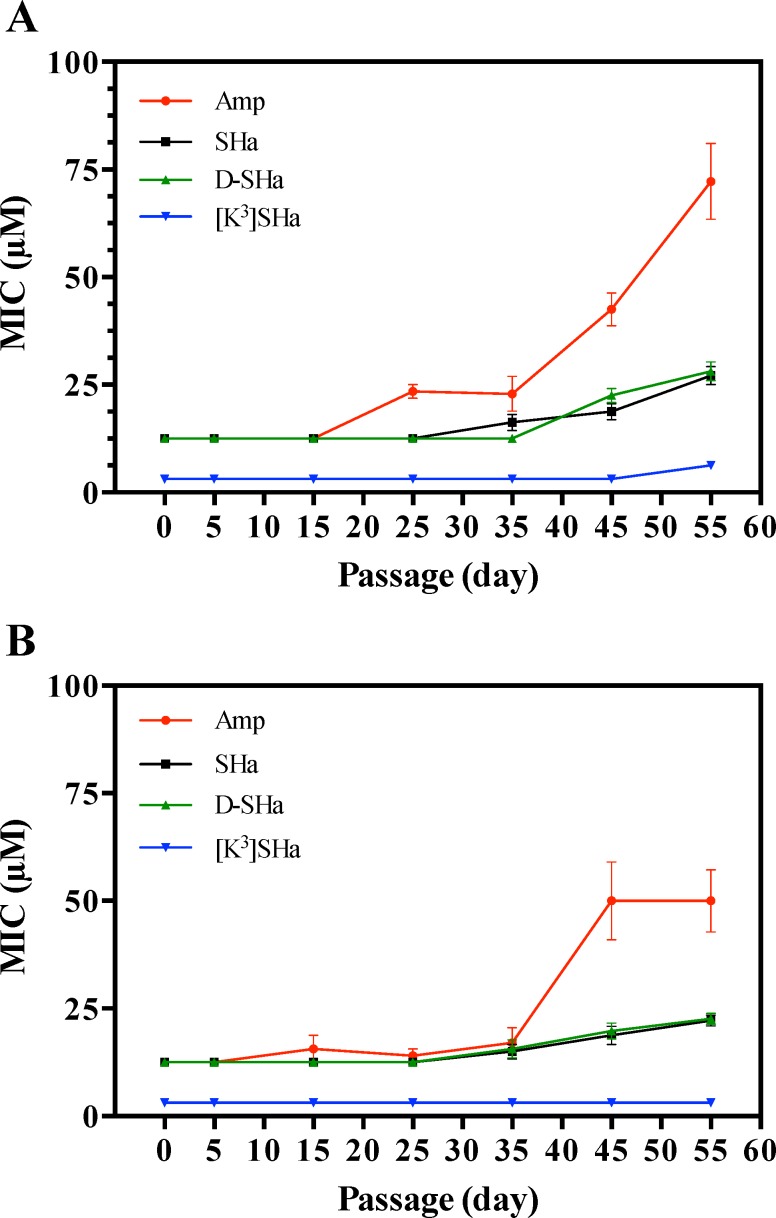
Fig 11. Multipassage resistance selection.
A, plot of MICs against E. coli lineages adapted to increasing concentrations of temporins or ampicillin. B, control: MICs against lineages grown in the same conditions without antimicrobial agents (MilliQ water). The following temporins were tested: SHa, D-SHa (SHa with all residues in D-configuration), and [K3]SHa. The conventional antibiotic ampicillin was also used for comparison. E. coli ATCC 25922 was continuously re-cultured in the presence of doubling concentrations of antimicrobial agents from 1/16 of the MIC until adaptation to the MIC (50 passages, 10 bacterial lineages with 1/16 MIC, 1/8 MIC, 1/4 MIC, 1/2 MIC, and MIC) (see Materials and Methods). The MIC of the antimicrobial agent was determined against the adapted E. coli lineages originating from different last passages: passage 5 (E. coli with no antimicrobial agent), 15 (E. coli with a concentration of antimicrobial agent equal to 1/16 MIC), 25 (1/8 MIC), 35 (1/4 MIC), 45(1/2 MIC), and 55 (MIC). MIC values were obtained in triplicate and represent the average of three independent experiments. Curves representing the MIC as a function of the passage number were obtained from the means ± SEM of MIC values of at least three independent experiments.