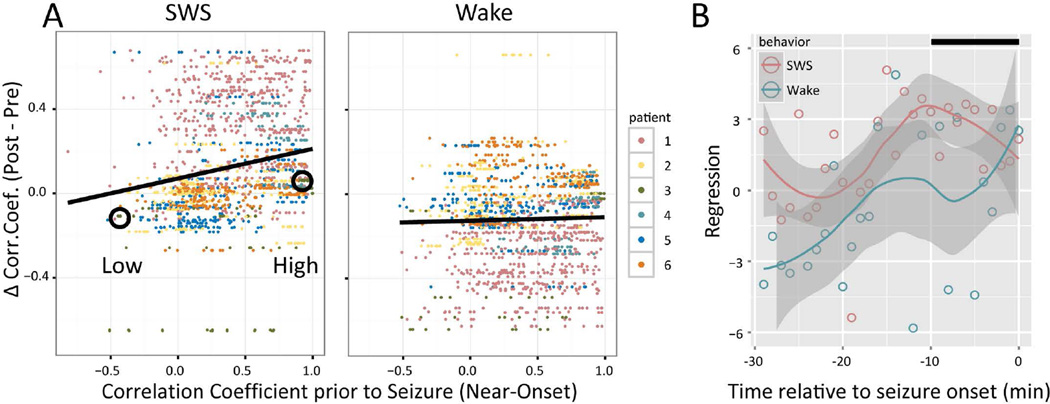
Figure 4.
Correlation coefficient of IIS show Seizure-Related Consolidation (SRC) specific to Slow-Wave Sleep (SWS). A. Each dot shows the difference (during Post epoch minus during Pre epoch) in correlation coefficient (CC) between two macroelectrodes as a function of the CC in the 10 min preceding seizures. Differences in CCs increased during SWS as function of the magnitude of CC prior to the seizure, but not during Wake ('*' p<.05, beta regression). Dot color denotes patient, as shown in the legend at right. B. Beta regression coefficients during SWS and Wake for 1 min "seizure" time bins relative to seizure onset. The Loess confidence interval (gray band) for Wake (cyan) never differs from zero for the entire 30 min window prior to seizure onset. The confidence interval for SWS (magenta), however, is greater than both zero and the Wake confidence interval for most of the 30 min prior to seizure onset, except for the last few minutes prior to onset, when the confidence intervals overlap. The black bar at upper right denotes the 10 min time window used to compute the values shown in panel A. Circles denote macroelectrode pairs that are used as examples in Figure 5.