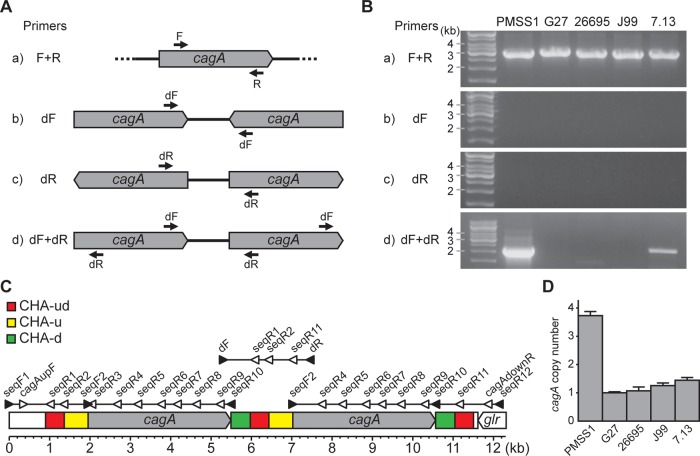
FIG 1 .
Analysis of cagA copy number by PCR and real-time PCR. (A) A scheme for the PCR-based method designed to detect multiple cagA genes and to identify the gene orientation. Primer annealing sites are shown. (B) H. pylori strains PMSS1, G27, 26695, J99, and 7.13 were analyzed for the presence of multiple copies of cagA using the four PCR sets. (C) A 12,374-bp region of PMSS1 was mapped on the basis of the DNA sequence of the cagA genes and their flanking regions. Primer annealing sites used for PCR (filled triangles) and for DNA sequencing (empty triangles) are indicated. Three repeated cagA homologous areas (CHAs) were designated CHA-ud (red), CHA-u (yellow), and CHA-d (green). (D) The cagA copy numbers of PMSS1, G27, 26695, J99, and 7.13 were analyzed by real-time PCR using the 2−ΔΔCT method. ureA was used as a reference gene, and G27 was used as a calibrator. The bar graphs indicate the average cagA copy number of each strain, and error bars represent standard deviations, derived from results of 4 independent experiments.