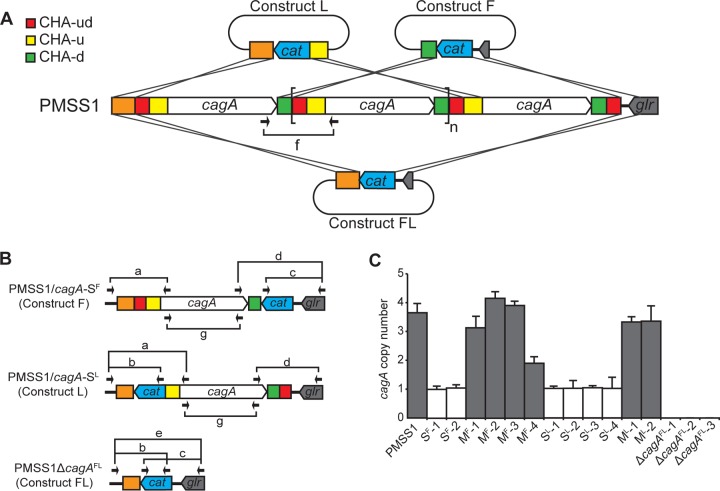
FIG 2 .
Generation and screening of PMSS1 isogenic mutant strains and determination of cagA copy number. (A) PMSS1 isogenic mutant strains were generated by transformation of PMSS1 with three different mutagenesis constructs: F, L, and FL. Putative homologous recombination events to generate cagA-SF, cagA-SL, and ΔcagAFL are illustrated. The three cagA homologous areas (CHAs) are indicated: CHA-ud (red), CHA-u (yellow), and CHA-d (green). A single cagA repeat is indicated with brackets. A subscript n indicates that the number of repeats is undetermined. (B) A PCR-based method was used to screen for the mutant strains cagA-SF, cagA-MF, cagA-SL, cagA-ML, and ΔcagAFL. Seven different PCRs (named a to g) were used for the screen; results from PCR f, which identified multiple cagA repeats, are denoted in panel A. The alignment sites of the primers are indicated with arrows, and the primers are listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material. (C) The cagA copy number was determined by real-time PCR using the 2−ΔΔCT method. ureA was used as a reference gene, and SF-1 was used as a calibrator. The bar graphs indicate the average cagA copy number of each strain, and error bars represent standard deviations, derived from results of 5 independent experiments.