Extended Data Figure 7. Defining schizophrenia risk genes based on functional annotation of credible SNPs.
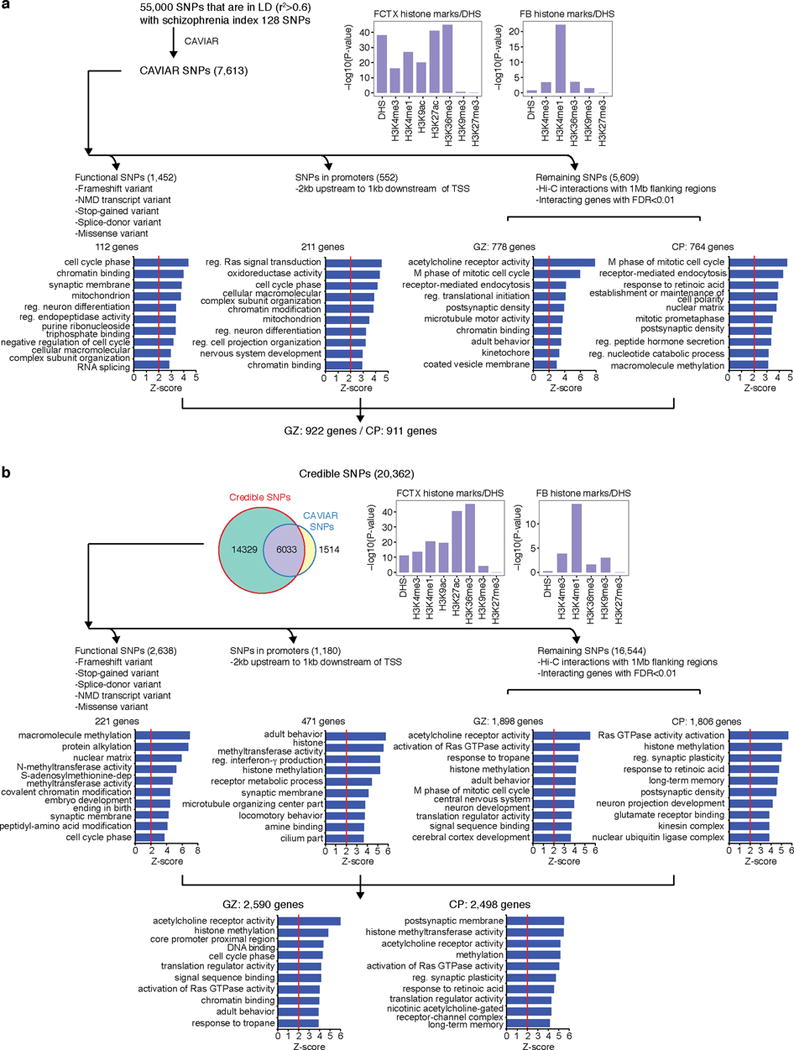
a, b, Credible SNPs identified by CAVIAR (a) and defined in the original study (b) are categorized into functional SNPs, SNPs that fall onto gene promoters, and un-annotated SNPs. DHS and histone marks enrichment of credible SNPs was assessed in fetal brain (FB) and adult frontal cortex (FCTX). Functional SNPs and promoter SNPs were directly assigned to the target genes, while un-annotated SNPs were assigned to the target genes via Hi-C interactions in CP and GZ. GO enrichment for genes identified by each category is shown in the bottom. Note that two credible SNP lists overlap with each other; credible SNPs defined in the original study are not restricted to genome-wide significant loci, so they include broader range (20,362 credible SNPs vs 7,547 CAVIAR SNPs) of SNPs than CAVIAR credible SNPs. NMD, nonsense-mediated decay.
