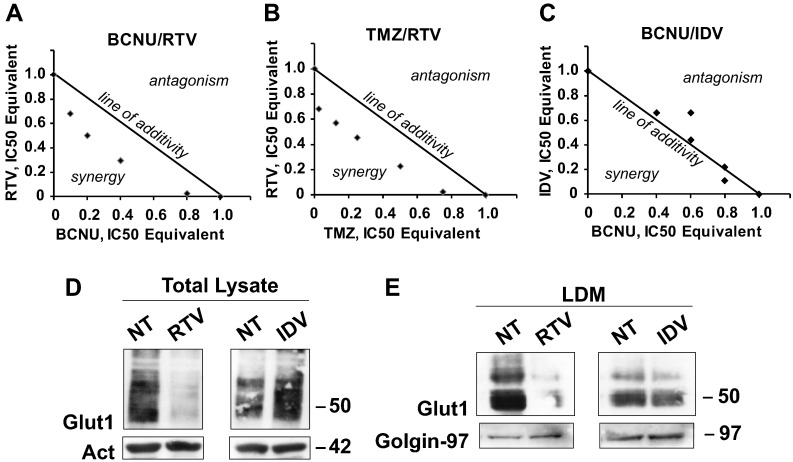
Figure 4.
(A) Isobolograms analysis of inhibition of growth of U87MG cells (A-C) and effects of RTV and IDV treatment on GLUT1/SLC2A1 transporter levels in U87MG cells (D-E). (A-C) The “line of additivity” connects the values of the IC50 of the two drugs used in combination, thus separating the quadrant into two parts; points plotted below the line of additivity indicate synergy (activity of the combination is larger than expected for the simple combination of the two drugs), whereas points above the line indicate antagonism (activity of the combination is lower than the expected for the simple combination of the two drugs). BCNU-RTV: (A) The two drugs at all tested concentrations show synergic activity. TMZ-RTV: (B) The two drugs at all tested concentrations show synergic activity. BCNU-IDV: (C) The two drugs show addictive or antagonistic behavior at all concentrations except for the highest, when we obtained an indication of minimal synergic activity. (D) Western blot of total lysates of U87MG cells: RTV reduced the level of GLUT1/SLC2A1 immunoreactivity, whereas IDV increased GLUT1/SLC2A1 level compared with untreated cells (NT). The same membrane was stripped and reacted with an antibody against actin (Act) whose level was similar in all samples. (E) As in D, but the cells were fractionated, and only the fraction containing the LDMs, where the GLUTs-containing vesicles reside, was analyzed by Western blot. As in the total extract, the GLUT1/SLC2A1 signal was decreased only by RTV treatment. The same membrane was stripped and reacted with an antibody against Golgin-97 whose level was similar in all samples. Numbers indicate the molecular weights in kDa.