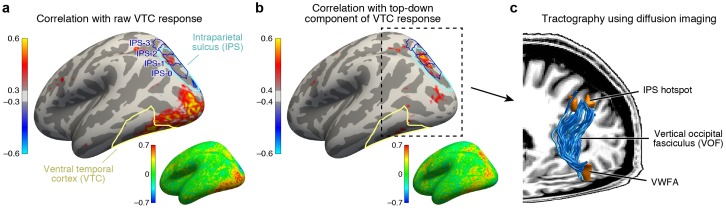
Figure 4. IPS is the source of top-down modulation to VTC.
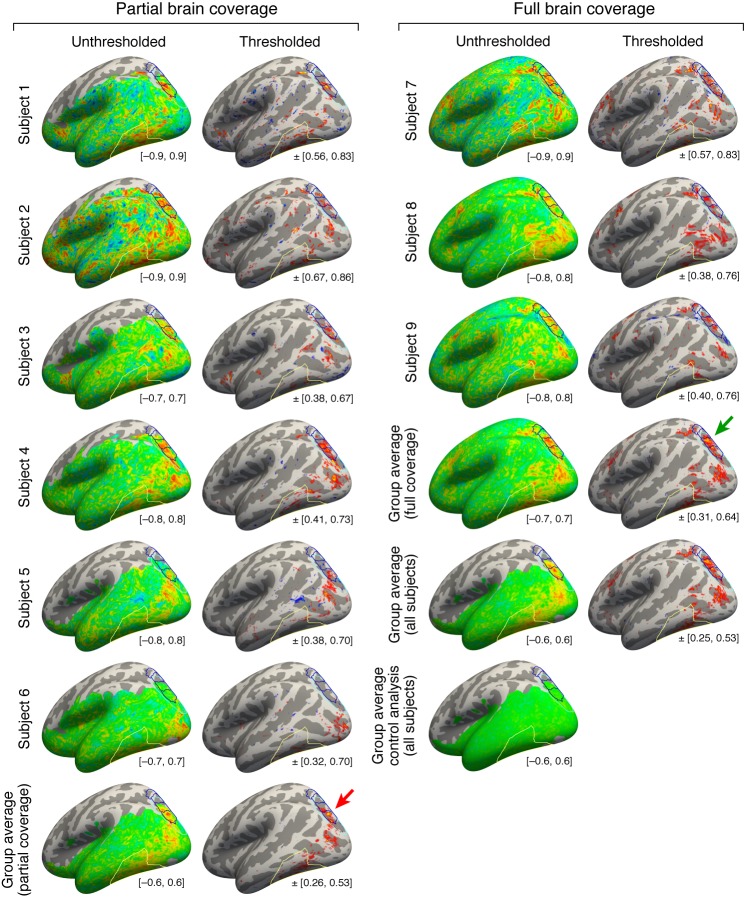
(a) Correlation with raw VTC response. This map depicts the correlation between the VTC response observed during the categorization and one-back tasks with the response at each cortical location (inset shows an unsmoothed and unthresholded map). Positive correlations are broadly distributed across occipital cortex. Results are shown for subjects with whole-brain coverage (n = 3); results for other subjects with partial-brain coverage (n = 6) are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. (b) Correlation with top-down component of VTC response. After removing bottom-up responses (fixation task), the correlation is spatially localized to a hotspot in IPS-0/1. (c) Tractography using diffusion MRI. We find that the vertical occipital fasciculus (Yeatman et al., 2014) connects VWFA and FFA to the IPS hotspot in each subject for which diffusion data were collected (n = 8) (rendering shows a representative subject).