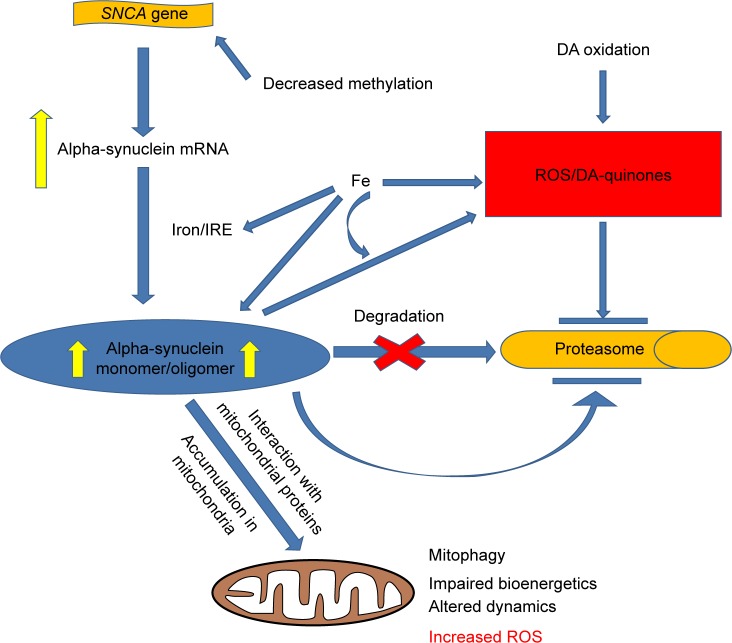
Figure 2.
Pathways of α-synuclein accumulation and toxicity in PD.
Notes: The accumulation of excess α-synuclein occurs in the PD brain through diminished degradation, increased transcription of SNCA and iron/IRE-regulated posttranscriptional mechanisms. Alpha-synuclein (monomers and oligomers) have multiple interactions with mitochondria, causing dysfunction of the organelle and increasing ROS production. Iron and DA-oxidation products contribute to oxidative stress in the PD brain, which is further enhanced by iron–α-synuclein interactions. The arrows indicate interactions, but arrows with end bars suggest inhibition.
Abbreviations: DA, dopamine; IRE, iron-responsive element; PD, Parkinson’s disease; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SNCA, α-synuclein gene.