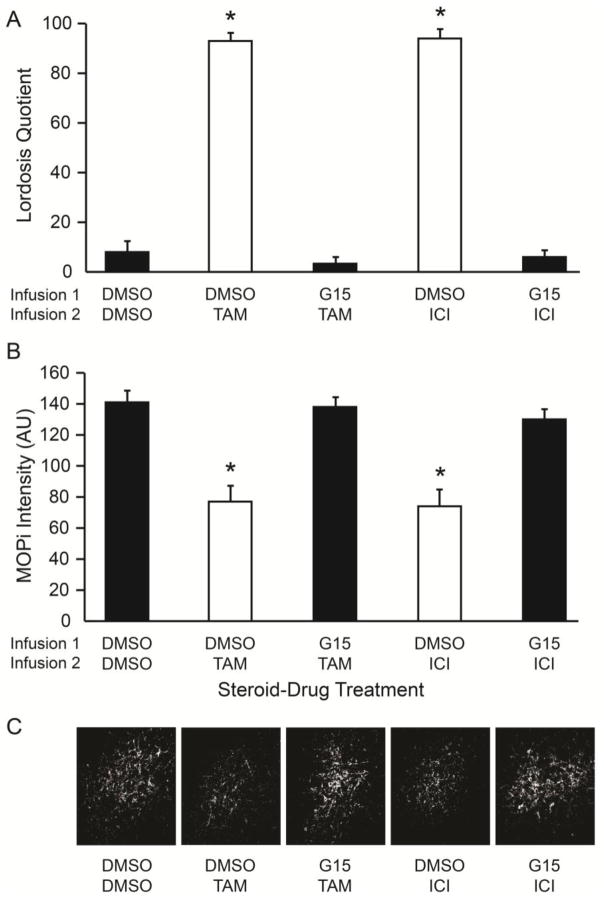
Fig 2.
Tamoxifen (TAM) and ICI 182,780 (ICI) rapid facilitation of lordosis and deactivation of MPN MOP was blocked by inhibition of ARH GPER. OVX rats primed with 2 μg EB received infusions into the ARH sequentially at 47.25 (Infusion 1), and 47.5 h (Infusion 2) post EB. Thirty minutes after the Infusion 2, each rat was tested for sexual receptivity as measured by lordosis quotient (LQ). On the next EB cycle, animals were given the same treatments and brains collected to measure the relative MPN MOP activation levels using MOP immunoreactivity (MOPi) staining intensity levels in arbitrary units (AU). A) TAM and ICI infused rats had a significantly increased LQ compared to DMSO controls, and administration of GPER antagonist, G15, prior to TAM or ICI significantly reduced the LQ compared to TAM or ICI only treated rats. B) Infusion of TAM and ICI significantly reduced MPN MOPi intensity levels compared to DMSO controls, and pretreatment with G15 prior to TAM or ICI blocked the reduction observed with TAM or ICI only treatment. C) Photomicrographs illustrating examples of MPN MOPi fiber densities for each treatment group used for MOPi intensity measures after contrast and brightness manipulation. ✱ = significantly different than other groups (p < 0.001).