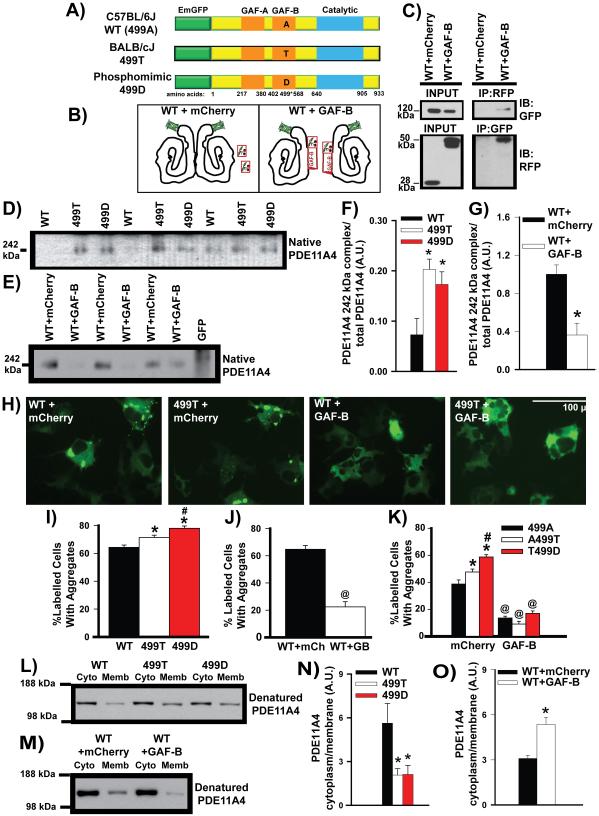
Figure 3. A nonsynonymous coding SNP in the PDE11A4 GAF-B domain promotes PDE11A4 homodimerization and alters PDE11A4 compartmentalization.
The PDE11A rs27963339 polymorphism affecting amino acid 499 results in an alanine (499A) in C57BL/6J mice (referred to as wild-type (WT) as this is the sequence published in NCBI) and a threonine (499T) in BALB/cJ mice. A) COS-1 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding an EmGFP-PDE11A4 fusion protein containing a WT 499A, 499T, or 499D (i.e., a phosphomimic aspartate). B) Alternatively, WT PDE11A4 was co-transfected with either mCherry alone or an isolated GAF-B domain fused to mCherry. Hypothetical structure of PDE11A4 based on [81]. C) Co-immunoprecipitation shows that the isolated GAF-B domain binds full-length PDE11A4, enabling the isolated GAF-B domain to act as a dominant negative that prevents homodimerization. D,F) Native PAGE shows that the 499T and 499D mutations increase expression of the presumed homodimer at 252 kDa (n=4/group); whereas, E,G) expression of the isolated GAF-B domain decreases expression of the presumed homodimer (n=6/group). Note: The difference in intensity between the WT vs WT-mCherry groups is not related to the co-expression of mCherry but rather reflects the fact that the experiments were conducted separately and different film exposures were necessary for each experiment in order to keep each group of samples within the linear range of the film (e.g., if WT and WT-mCherry exposures were kept constant between experiments, then the 499 groups would be overexposed). H, I) Consistent with these opposing effects on homodimerization, 499T and 499D promote aggregation of PDE11A4 in COS-1 cells (n=8/group); whereas, J) the isolated GAF-B domain decreases aggregation (n=6/group). K) Importantly, the ability of 499T and 499D to promote PDE11A4 aggregation is blocked when homodimerization is prevented by the isolated GAF-B domain (n=8/group), which suggests the ability of 499T and 499D to increase homodimerization is directly related to their ability to promote the trafficking of PDE11A4 into aggregates. L, N) Biochemical fractionations show that 499T and 499D shift PDE11A4 from the cytosol to the membrane relative to WT PDE11A4 (n=5/group), mimicking PDE11A4 compartmentalization in the VHIPP of BALB/cJ vs. C57BL/6J mice. M,O). In contrast, disrupting homodimerization with the isolated GAF-B domain shifts PDE11A4 from the membrane to the cytosol (mCherry, n=13; GAF-B, n=9). The fact that 499T and 499D behave similarly suggests the 499T construct is naturally phosphorylated in COS-1 cells. Post hoc, *vs. WT, P<0.05-0.001; #vs. 499T, P=0.037-0.011; @vs. mCherry, P<0.001. A.U.—arbitrary units. Note that all n’s reflect biological replicates. Data passed normality and equal variance and are graphed as means ±SEM. Brightness and contrast adjusted for graphical clarity of images.