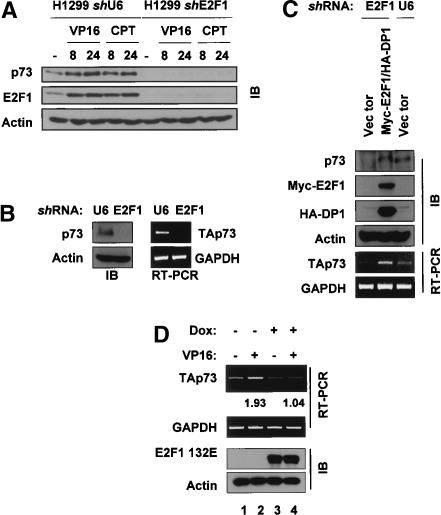
Figure 5.
E2F1 regulates basal and DNA-damage-induced levels of p73 mRNA and protein. (A) H1299 cells stably transfected with either empty vector (U6) or a vector expressing an anti-E2F1 shRNA (E2F1) were treated with VP16 or camptothecin (CPT) and immunoblotting was performed for p73, E2F1, and actin. (B) Asynchronously growing H1299-shU6 and H1299-shE2F1 cells were collected for Western blotting (left) or RT-PCR for p73 (right). (C) Empty vector or constructs expressing 6myc-E2F1 and HA-DP1 were cotransfected into H1299-shE2F1 cells (E2F1 lanes) and 24 h later extracts were prepared for immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies or RT-PCR for p73 and GADPH. Protein lysates or RNA from H1299-shU6 cells (lane labeled U6) were included for comparison of p73 levels in H1299 cells. (D) Saos2 cells expressing E2F1 132E under the control of a doxycyline (dox)-inducible promoter were exposed to 2 μg/uL dox for 24 h before the addition of 10 μM VP-16 for 24 h. Parallel cultures were collected for RT-PCR and Western blotting as above. Numbers indicate fold inducion of p73 after DNA damage as determined by densitometry.