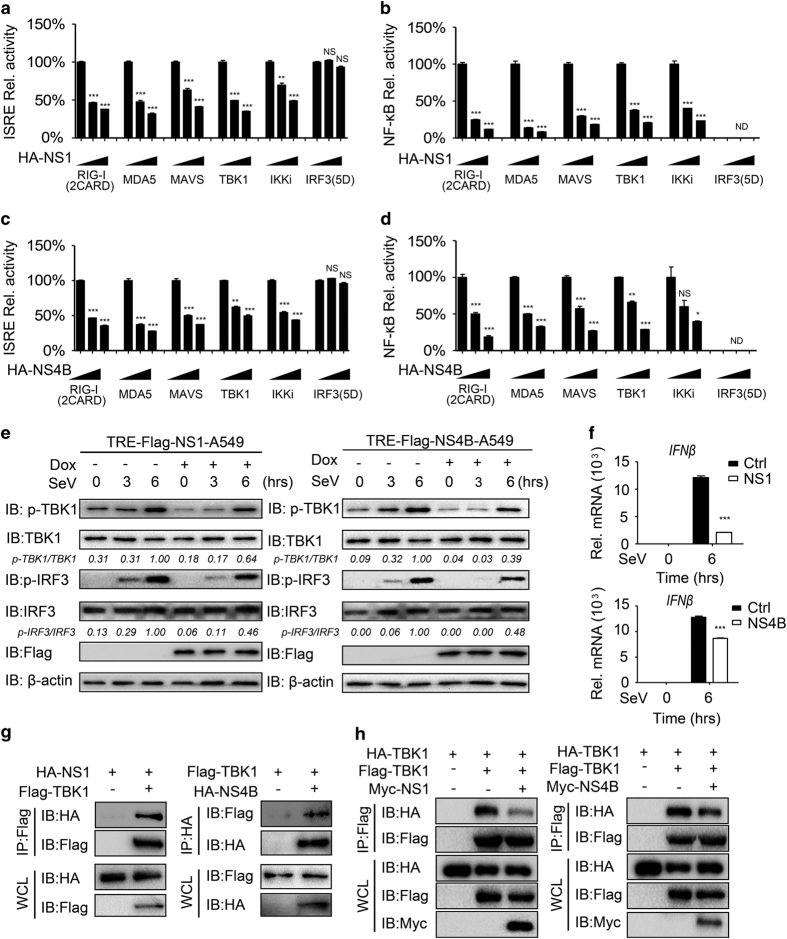
Figure 2.
NS1 and NS4B inhibit type I IFN signaling by targeting TBK1. (a, b) Luciferase activity in 293T cells transfected with an ISRE luciferase reporter (a) or NF-κB luciferase reporter (b), together with vectors for RIG-I (2CARD), MDA5, TBK1, IKKi and IRF3 (5D), along with empty vector or with expression vectors for NS1. (c, d) Luciferase activity in 293T cells transfected with an ISRE luciferase reporter (c) or NF-κB luciferase reporter (d), together with vectors for RIG-I (2CARD), MDA5, TBK1, IKKi and IRF3 (5D), along with empty vector or with expression vectors for NS4B. (e) Immunoassay of extracts of NS1- or NS4B-inducible A549 cells were treated with doxycycline (Dox; 200 ng ml−1) for 24 h, followed by SeV (MOI=0.1) for the indicated time points. (f) Quantitative PCR with reverse transcription analysis of IFNβ mRNA in NS1- or NS4B-inducible A549 cells pretreated with Dox (200 ng ml−1), followed by SeV (MOI=0.1) infection for 4 h. (g) Co-immunoprecipitation and immunoassay of extracts of 293T cells transfected with Flag-TBK1 and HA-NS1 (left) or HA-NS4B (right). (h) Co-immunoprecipitation and immunoassay of extracts of 293T cells transfected with Flag-TBK1, HA-TBK1 and Myc-NS1 or NS4B. Data in a–d and f are expressed as means±s.d. of at least three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. ND, determined; NS, not significant.