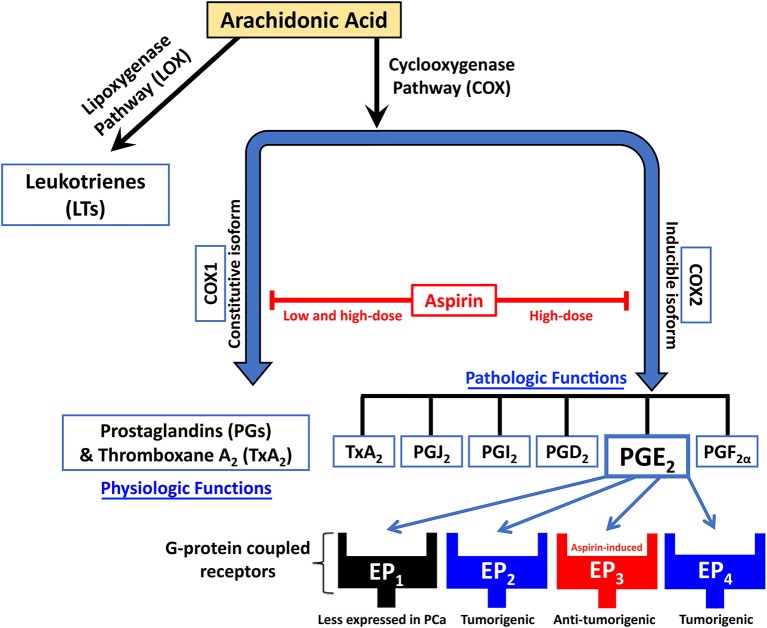
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing the mechanism of action of NSAIDs like aspirin in inhibiting the metabolism of arachidonic acid by blockade of the cyclooxygenases (COX) pathway and the prostaglandins (PG) synthase pathway, thus suppressing PGs synthesis. Aspirin also works by upregulating EP3, an inhibitory G-protein-coupled receptor of the prostaglandin PGE2.